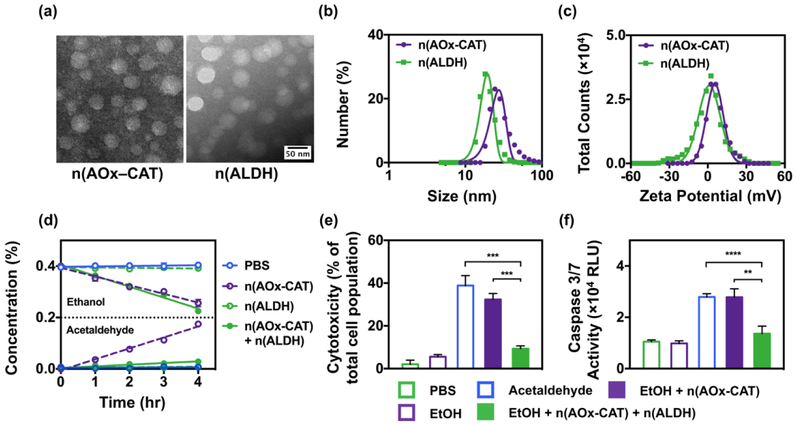
Figure 2.
Characterization of the nanocapsules. (a) Transmission electron microscopy images of n(AOx–CAT) and n(ALDH) with uniform diameters of 32.8±4.0 nm and 34.3±3.9 nm, respectively. (b) Size and (c) Zeta potentials of n(AOx–CAT) and n(ALDH) measured by dynamic light scattering. (d) The kinetics of the removal of alcohol and acetaldehyde in a closed system containing alcohol (0.4%, w/v), after incubating with PBS, or n(AOx–CAT) (0.8 U/mL), or n(ALDH) (6.0 U/mL), or the mixture of n(AOx–CAT) and n(ALDH) for 4 hr. (e) Reduced cytotoxicity in primary mouse hepatocytes (PMH) after the simultaneous removal of alcohol and acetaldehyde. Cytotoxicity was assessed by measuring the release of lactate dehydrogenase. (f) Reduced apoptosis in PMH after the simultaneous removal of alcohol and acetaldehyde. Apoptosis was indicated by the relative luminescent unit (RLU) of Caspase 3/7 activity. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n=3~6). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005 and ****P < 0.0001.