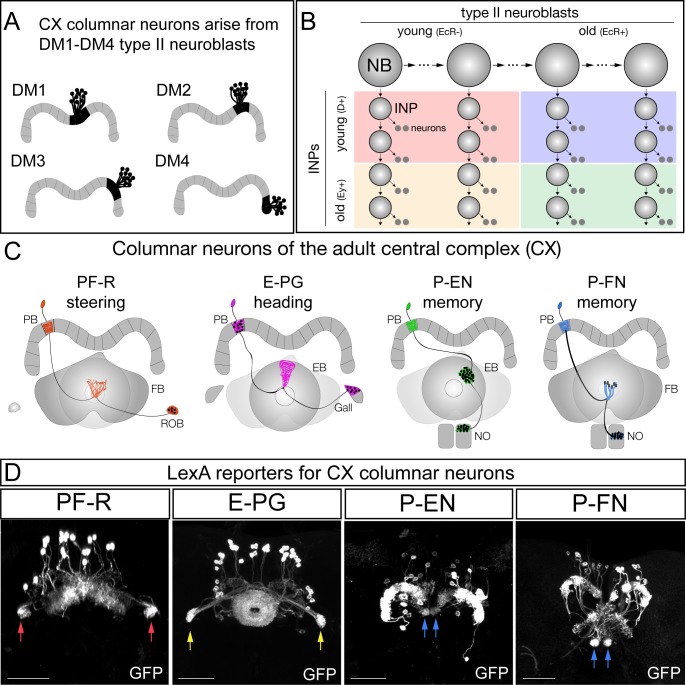
Figure 1. CX columnar neurons are generated by type II neuroblast lineages.
(A) CX columnar neurons innervating the PB originate specifically from each of four bilateral type II neuroblast lineages (DM1-DM4), which include all four neuronal subtypes shown in panel D. DM1 lineage neurons innervate the most medial PB glomeruli, and DM4 lineage neurons innervate the most lateral PB glomeruli. Adult brain right hemisphere shown. (B) Type II neuroblasts divide every 1.6 hr to generate ~60 INPs; each INP progeny divides every 2–3 hr to produce 10–12 neurons (Homem et al., 2013). Both neuroblasts and INPs express temporal transcription factors that subdivide their lineages into distinct molecular windows. Finer subdivisions exist but are not shown for clarity. (C) PF-R, E-PG, P-EN, and P-FN columnar neuron subtypes; each has a proposed function in navigation (Stone et al., 2017; ) and a distinct pattern of connectivity. PB, protocerebral bridge; FB, fan-shaped body; ROB, round body; EB, ellipsoid body; NO, noduli. (D) Adult CX columnar neurons derived from INPs labeled with adult LexA lines specific for each subtype; see Figure 1—figure supplement 1A for genetic details. ROB, red arrows; Gall, yellow arrows; Noduli, blue arrows. Scale bars, 40µm. Genotypes: PF-R, UAS-FLP; R9D11-Gal4, R37G12-lexA; lexAop(FRT.stop)mCD8::GFP; E-PG, UAS-FLP; R9D11-Gal4, R60D05-lexA; lexAop(FRT.stop)mCD8::GFP; P-EN, UAS-FLP; R9D11-Gal4, R12D09-lexA; lexAop(FRT.stop)mCD8::GFP; P-FN, UAS-FLP; R9D11-Gal4, R16D01-lexA; lexAop(FRT.stop)mCD8::GFP.