Fig. 1. Magnetic and transport properties of Fe2V0.9Cr0.1Al0.9Si0.1.
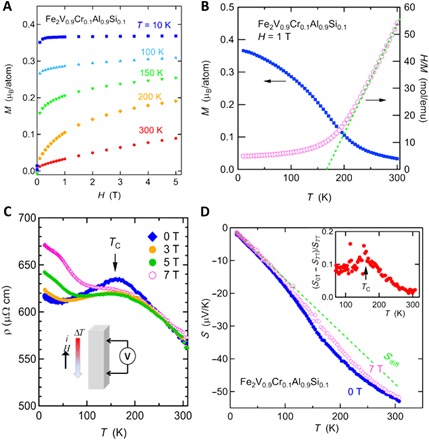
Measured under magnetic fields H as functions of temperature T. (A) The compound shows a ferromagnetic ordering with a small saturation magnetization of 0.4 μB per magnetic atom, indicating weak itinerant ferromagnetic state. (B) M versus T data show that ferromagnetic ordering occurs below TC = 160 K. The inverse magnetic susceptibility H/M shows a T linear dependence above TC, indicating a Curie-Weiss behavior H/M = (T − θ)/C, where θ is the Weiss temperature and C is the Curie constant (shown as a broken line). From the fitting, θ = 167 K and the effective magnetic moment peff = 4.26 μB per atom are obtained, where the magnetic atoms are Fe or Cr. (C) Electrical resistivity ρ shows a cusp-like anomaly at TC. This behavior is suppressed by magnetic fields. Inset: The configuration for transport measurements in magnetic fields. (D) Seebeck coefficient S measured at 0 and 7 T. S exhibits a shoulder-like enhancement around TC, and the enhancement is suppressed by magnetic field. At H = 7 T, S(T) becomes closer to the linear T behavior as is expected for a normal degenerate semiconductor. Inset: The difference of S between H = 0 and 7 T with respect to the values at 7 T, which exhibits a peak at TC, indicating a strong effect of spin fluctuation.
