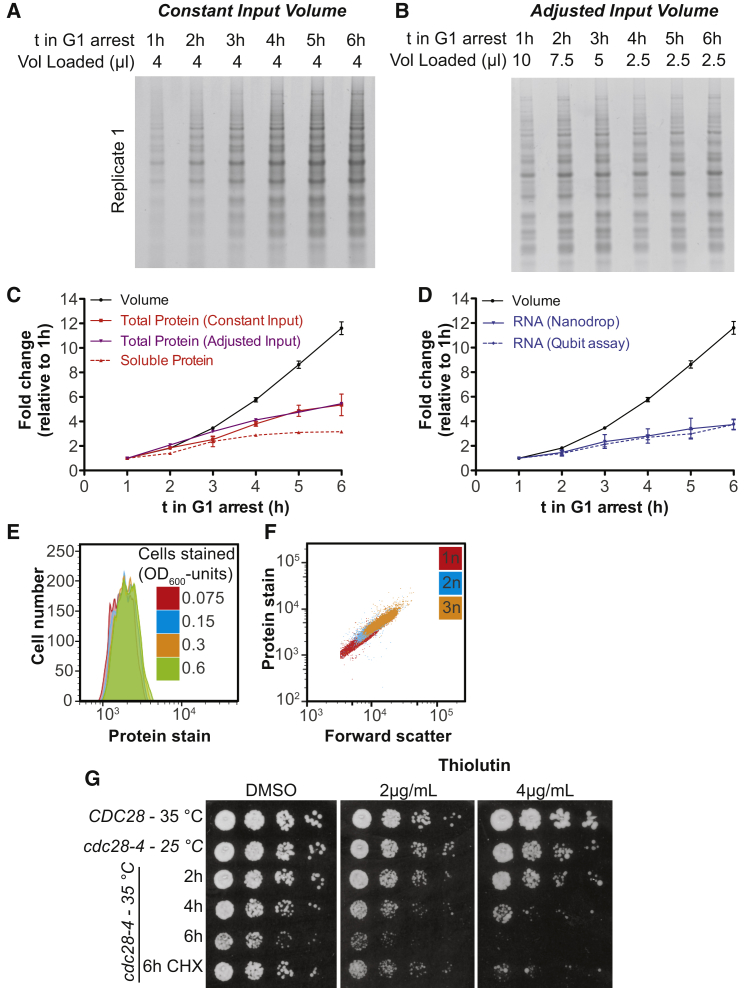
Figure S5.
Cellular Protein and RNA Quantification during Prolonged G1 arrest, Related to Figure 3
(A–C) Newborn cdc28-13 cells were isolated by centrifugal elutriation and arrested in G1 at 37°C. Equal numbers of cells were collected and total protein was isolated by TCA precipitation of cells, followed by mechanical cell lysis in 8M urea and boiling extracts in 3% SDS. (A) Equal volumes of lysate were run on SDS-PAGE followed by Comassie blue staining. Three biological replicates were performed. (B) Different volumes of extract were loaded as indicated to reduce potential effects of non-linearity in the assay. This gel was used to quantify total protein content for Figure 3C. (C) Quantification of total protein from (A, red) and (B, purple). Soluble protein was extracted by breaking cells in Tris/NaCl (without detergent, complete cell lysis was confirmed microscopically) followed by centrifugation (20 min/21000×g) to clear the lysate. 3 biological replicates were analyzed for cells arrested at 37°C for 1 h, 3 h and 5 h. Protein concentration was analyzed using the Bradford protein assay. Cell volume was measured on a coulter counter (the same data for total cell volume, total protein determined with adjusted input and one replicate of soluble protein quantification are shown in Figure 3C).
(D) Same experiment as in (A–C), but isolation of total cellular RNA by phenol extraction followed by ethanol precipitation and column purification. Quantifications were performed before (Qubit assay) and after (Nanodrop) column purification of the RNA.
(E and F) cdc28-13 cells were fixed with formaldehyde and subsequently permeabilized in 70% ethanol. Cells were stained with a primary amine reactive dye (Alexa Fluor NHS Ester) to stain total cellular protein and analyzed by flow cytometry. (E) Different numbers of logarithmically growing cells were stained. Cell number is indicated in units of optical density, which correlates with biomass. For logarithmically growing cells, one OD600 unit corresponds to roughly 2∗107 cells. The same concentration and volume of dye was used for all samples. This analysis shows that the dye does not become limiting. (F) 0.15 OD600 units of logarithmically growing haploid (1n), diploid (2n) and triploid (3n) cells were stained. This analysis confirms that this assay can distinguish protein content in differently sized cells. In addition, it shows that in logarithmically growing cells protein content and forward scatter (an estimate of cell size) correlate.
(G) CDC28 and cdc28-4 mutant cells were arrested at 35°C under the indicated conditions. Ten-fold serial dilutions were plated and grown at 25°C on YEPD (2% glucose) or YEPD supplemented with the pan RNA polymerase inhibitor Thiolutin.