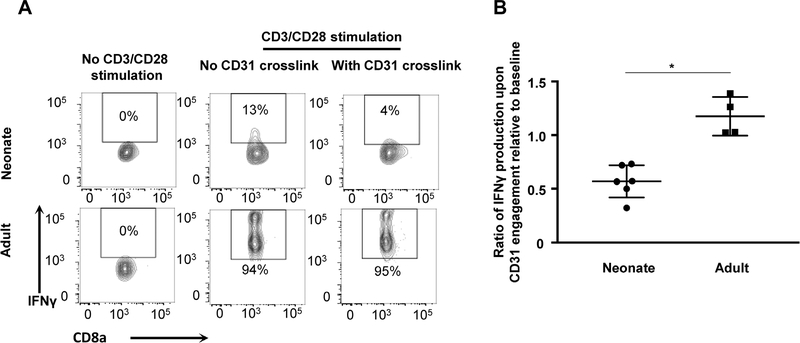
FIGURE 5. CD31 signals decreased IFN-γ production in neonatal CTLs upon in vitro stimulation.
Naïve splenocytes were isolated from neonatal and adult mice and were activated by CD3 and CD28 co-stimulation for 48 h and then CD31 crosslinking was performed. (A) Representative flow plots depicting the frequency of IFN-γ+ effector CTLs without stimulation (left), with CD3/28 stimulation and no CD31 crosslink (middle) and with CD3/28 stimulation and CD31 crosslink (right) for neonatal animals (top panels) and adult animals (bottom panels). (B) Ratio of IFN-γ production upon CD31 crosslink relative to baseline after in vitro T cell stimulation with anti-CD3/28 (n = 4–8 animals per group, 2 independent experiments). Mann-Whitney (nonparametric) statistics were used to compare neonate to adult (*P < 0.05)