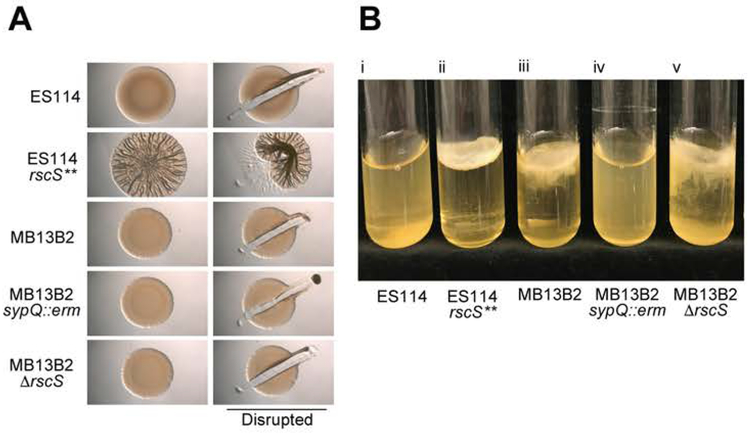
Fig. 5.
In vitro biofilm phenotypes. (A) Development of a wrinkled-colony morphology over time. Ten microliters of a culture of each of three V. fischeri strains were spotted onto LBS agar plates. After 72 h of growth at 24 °C, colonies were disrupted with a toothpick to assess colony cohesiveness, which is an indicator of Syp-encoded polysaccharide production (Yip et al., 2005; Yip et al., 2006). (B) Pellicle formation in static liquid culture. Five strains of V. fischeri [(i) ES114, (ii) ES114 rscS** (KV4366), (iii) MB13B2, (iv) MB13B2 ΔsypQ (KV8195), and (v) MB13B2 ΔrscS (CBNR107)] were inoculated into 5 ml of LBS broth, and grown to log phase under shaking conditions. Cultures were then incubated statically at 24 °C for 10 days, and assessed for the presence of a surface pellicle.