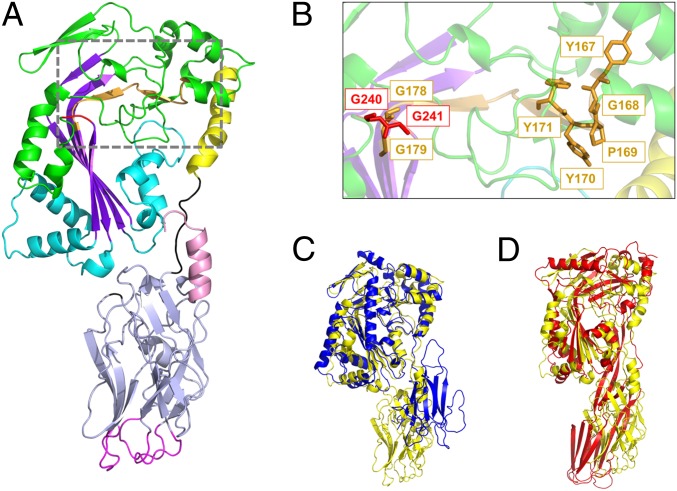
Fig. 1.
Crystal structure of GNIP1Aa in ribbon representation. The figure was made with PyMOL (33). (A) The structure of GNIP1Aa is composed of two domains. The N-terminal MACPF domain is colored green with key structural features shown in different colors: central four-stranded β-sheet in purple; two clusters of helices, CH1 and CH2, in cyan; and MACPF-conserved α-helix in yellow. Additionally, the signature MACPF motif and two conserved glycines are highlighted in orange and red, 167YGPYYX6GG179 and 240GG241, respectively. The linker between the two domains is shown in black. The C-terminal domain is colored light blue with an exception of three apical loops in magenta and the C-terminal tail in pink. (B) Close-up of the conserved MACPF residues, 167YGPYYX6GG179 and 240GG241, shown in stick presentation in orange and red, respectively. (C) Superposition of GNIP1Aa structure in yellow with bacterial MACPF protein from P. luminescens (PDB ID code 2QP2) in blue; RMSD of 2.3 Å for 298 Cα positions. (D) Superposition of GNIP1Aa structure in yellow with a representative of CDCs, perfringolysin O (PDB ID code 1M3I) in red; RMSD of 4.1 Å for 209 Cα positions.