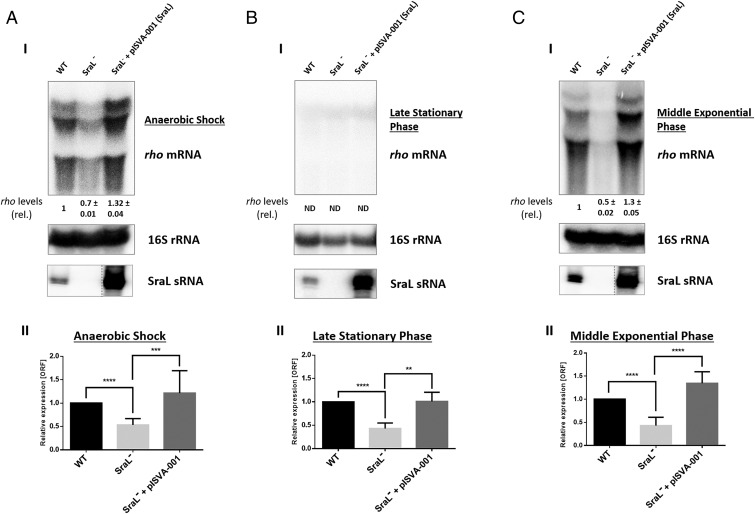
Fig. 1.
rho mRNA regulation by SraL sRNA in different growth conditions. Total cellular RNA was extracted from Salmonella strains indicated in the figure. The following conditions were used: (A) Cells were grown in LB at 37 °C and 220 rpm to an OD600 of 0.3 and then placed in a filled 50-mL Falcon tube and incubated at 37 °C without agitation during 30 min (AS). (B) Cells were grown in LB at 37 °C and 220 rpm until 6 h after OD600 of 2 (late stationary phase). (C) Cells were grown in LB at 37 °C and 220 rpm until OD600 of 1 (middle exponential phase). (I) (Upper) Twenty micrograms of total RNA were separated on a 1.3% formaldehyde/agarose gel. The gel was then blotted to a Hybond-N+ membrane and hybridized with the corresponding rho riboprobe. The transcripts were quantified using ImageQuant software. The amount of RNA in the wild type was set as one. The ratio between the amounts of RNA of each strain and the wild type is represented (relative levels). A representative membrane is shown, and the values indicated correspond to the average of several Northern blot experiments with RNAs from at least two independent extractions. The membrane was stripped and then probed with 16S rRNA as loading control. (Lower) Fifteen micrograms of total RNA were separated in a 6% PAA/8.3 M urea to determine the expression level of SraL; contrast of SraL−+pISVA-001 was adjusted separately as indicated by the dashed line. (II) The transcriptional level of rho was also determined by quantitative real time-PCR analysis using Rotor-Gene 3000 (Corbett) system and with cDNA synthesized from 1 µg of purified RNA. Values are shown relative to the expression levels in wild-type strain. Results were normalized with the expression of the housekeeping gene 23S rRNA and represent at least three independent experiments. ****P < 0.0001, ***P ≤ 0.0005, **P < 0.001 by Student’s t test.