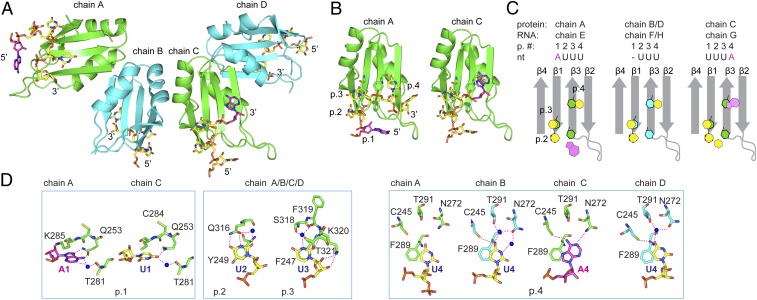
Fig. 2.
Crystal structure of HuR RRM3 in complex with RNA shows homodimers and canonical RNA recognition. (A) Cartoon representation of the four RRM–RNA molecules (RRM chains A to D and RNA chains E to H) in one asymmetric unit. Chains A:B (green:cyan) and C:D (green:cyan) represent the same dimer interface. RNA is shown in stick representation, with carbons of uridines in yellow and carbons of adenines in magenta. (B) RRM3 of chains A and C. RNP side chains and RNA are shown in stick representation. Binding pockets are abbreviated as “p.” (C) A schematic representation of the RNP arrangement is colored in gray, uracils and adenines in yellow and magenta, respectively, and aromatic residues of the RNP in green (chains A/C) or cyan (chains B/D). Protein and RNA chains, pocket number (p. #), and nucleotides are shown (Top). (D) Protein–RNA contacts are shown as sticks for each chain. Chains are indicated (Top). Binding pockets are indicated (Bottom). (D, Left and Right) Interactions distinct to each chain in pockets 1 and 4. (D, Middle) Pocket 2 and 3 interactions representative of all four chains. Hydrogen bonds are shown as red dashed lines.