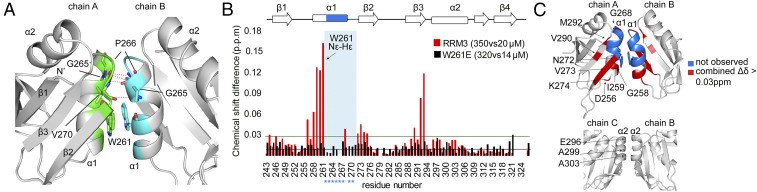
Fig. 4.
RRM3 dimerizes in solution via the conserved Trp261. (A) Cartoon representation of the RRM3 homodimer interface between RRM chains A and B. Amino acids involved in hydrophobic interactions are colored green (chain A) and cyan (chain B). The conserved W261 involved in stacking and other amino acids involved in hydrogen bonds are shown in stick representation. Hydrogen bonds are represented as dashed lines. (B) Comparison of the combined chemical shift perturbations of RRM3 and W261E, 350 vs. 20 μM (red) and 320 vs. 14 μM (black), respectively. Blue asterisks indicate amino acids located within dimerization helix 1 of which signals are missing in the 1H-15N HSQC of RRM3. The W261 side chain Nε-Hε was also included in the analysis (indicated by the arrow). The green and black horizontal lines represent the SD of all chemical shift differences for RRM3 and W261E, respectively. (C) Cartoon representation of the RRM3 homodimer (Top) (chains A and B) and the crystallographic dimer (chains B and C) (Bottom). Residues missing in the 1H-15N HSQC of the RRM3 spectrum are highlighted in blue, and residues showing ∆δ > 0.03 ppm are in red.