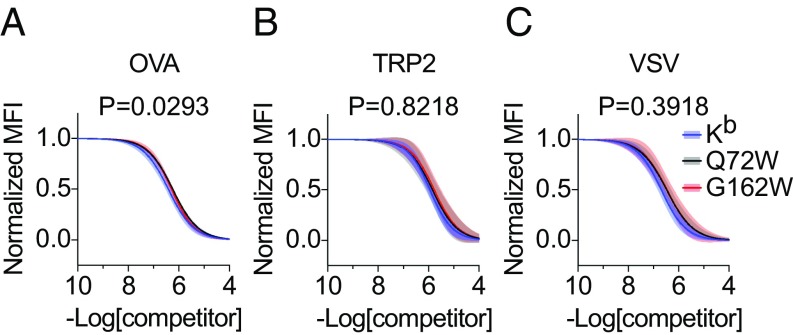
Fig. 3.
Kb mutants Q72W and G162W display unaltered peptide binding properties. (A–C) Stable L cell transfectants expressing Kb or Kb mutants Q72W and G162W were loaded with a biotinylated reference peptide SII[C-biotin]FEKL and increasing concentrations of unlabeled competitor peptides OVA257–264 (A), TRP2180–188 (B), and VSV52–59 (C). After peptide loading and staining with streptavidin-PE, flow cytometry was used to quantify reference peptide binding for each titration of competitor. Variable-slope, nonlinear regression was used to fit inhibition curves (solid lines), normalized by the maximum and minimum values, using two independent measurements at each competitor peptide concentration. Error bands represent the 95% confidence intervals (shaded) of the inhibition curves. R2 > 0.94 for all inhibition curves. The extra sum-of-squares F test was used to assess statistically significant differences among inhibition curves. The null hypothesis that Kb, Q72W, and G162W bound each competitor peptide equivalently was not rejected based on the multiple comparisons corrected significance threshold of P < 0.0167.