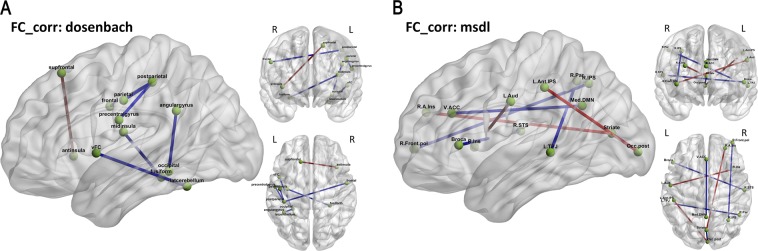
Fig. 6.
Key pathological alterations in schizophrenia suggested by top-most reliable features—network edges show elevated (red) and suppressed (blue) changes in functional connectivity. Panels show top 99th percentile of top functional connectivity features using dosenbach and msdl atlases. a Decreased functional connectivity between regions—left ventral frontal cortex and left lateral cerebellum, left occipital and left angular gyrus, left middle insula and right fusiform gyrus, and lastly left post parietal cortex with three nodes namely right frontal gyrus, left parietal, left precentral gyrus. Increased interhemispheric functional connectivity between left superior frontal gyrus and the right anterior insula. b Decreased functional connectivity between regions—striatum and posterior occipital lobe, right intraparietal sulcus and right frontal pole, ventral anterior cingulate cortex and medial default mode network, left temporo-parietal junction and right parietal cortex, right superior temporal sulcus and Broca’s area. Increased functional connectivity between regions—right anterior insula and striatum, right insula and left auditory cortex, and left anterior intraparietal sulcus and posterior occipital lobe