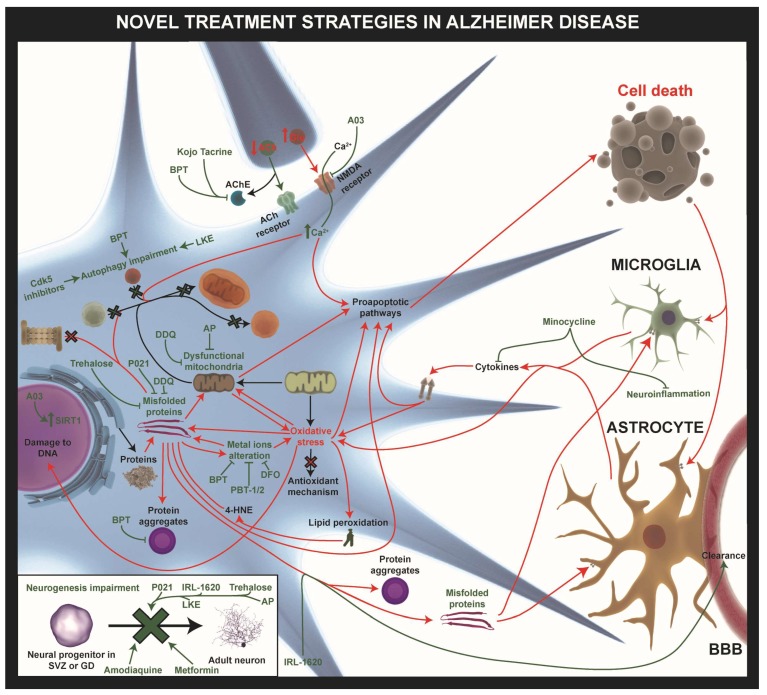
Figure 2.
Novel treatment strategies for AD. The most relevant approaches to restore altered pathways in AD are shown with green arrows when processes are improved or T-bars when inhibited. The novel acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors BPT and Kojo tacrine affect autophagy impairment, misfolded proteins, and their aggregates in the intracellular and extracellular brain environment. A03 compound has an antagonist influence on the NMDAR-mediated pathways involved in increasing SIRT1 expression. Other target strategies of autophagy impairment are CDK5 inhibitors and small lanthionine ketamine-ethyl ester (LKE) molecules against increased CRMP2 expression. Neurogenesis impairment is improved by P021, IRL-1620, trehalose, metformin, LKE, amodiaquine, and allopregnanolones (AP) (BR297) treatments. IRL-1620 increases the clearance of Aβ in the bloodstream by influencing the Endothelin B (ETB) receptor. P021 and trehalose have positive influences on misfolded proteins. Diethyl(3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamino) (quinolin-4-yl)methylphosphonate (DDQ) and AP (BR297) increase mitochondrial biogenesis and Aβ clearance. Minocycline increases anti-inflammatory responses and decreases pro-inflammatory responses. Metal ions homeostasis alteration can be rescued by PBT-1, PBT-2, 4-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)thiosemicarbazones (BPT) derivatives, and deferoxamine (DFO).