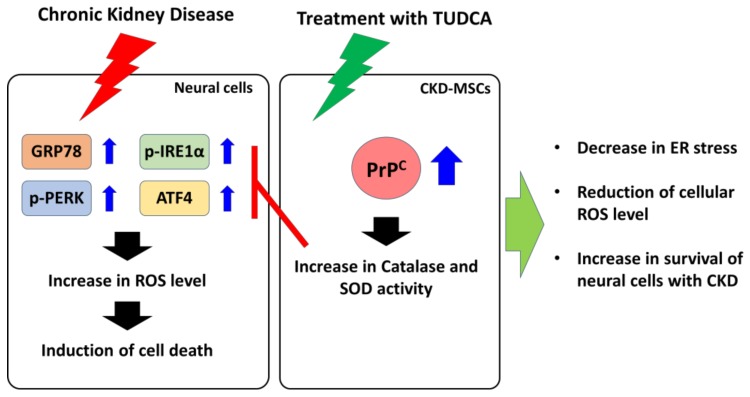
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the proposed mechanisms by which TUDCA-treated CKD-MSCs protect against neural cell apoptosis induced by CKD-mediated ER stress. TUDCA-treated CKD-MSCs induce the expression and secretion of PrPC, leading to increased levels of PrPC in neural cells. Under the presence of uremic toxin, the upregulation of PrPC inhibits CKD-mediated ER stress in neural cells through the induction of catalase and SOD activities, resulting in increased survival of neural cells in subjects with CKD. Blue array means that increase expression or activation of protein. Red “T” arrow means that block expression or activation of protein. Black array means cell signal pathway. Green arrow means TUDCA-treated CKD-MSCs finally protection pathway.