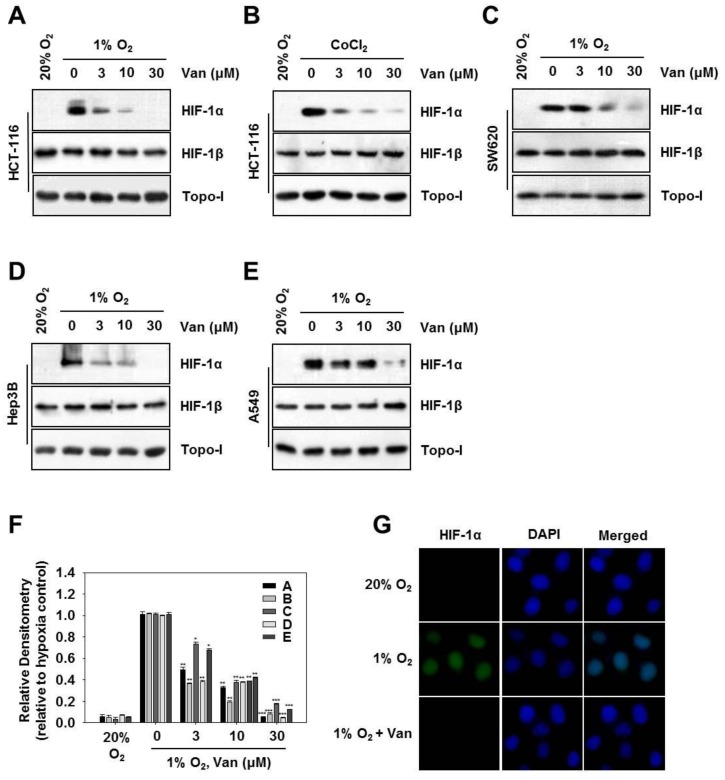
Figure 2.
Vanillic acid (Van) inhibits HIF-1α protein expression in a dose-dependent manner. (A,C–E) HCT116, SW620 cells, Hep3B, and A549 cells were pretreated without or with indicated concentration of vanillic acid (Van), then cultured under normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 12 h. Whole-cell lysates for HIF-1β and nuclear extract for HIF-1α were detected by Western blot. Anti-Topo-I antibody was used as a loading control. (B) HCT116 cells were cultured with the indicated concentration of vanillic acid (Van) for 30 min and treated with CoCl2 (200 µM). After 12 h incubation, the whole-cell lysates for HIF-1β and nuclear extract for HIF-1α was detected by Western blot. Anti-Topo-I antibody was used as a loading control. (F) Data were shown as mean ± SD (n = 3). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, compared with hypoxia control. (G) HCT116 cells cultured in chamber slides, then were treated with or without vanillic acid (Van, 30 µM) under normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 12 h. The left column shows the HIF-1α protein in green fluorescence. The middle column shows nuclei stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue fluorescence). The right column shows the merged images. Magnification = 400×.