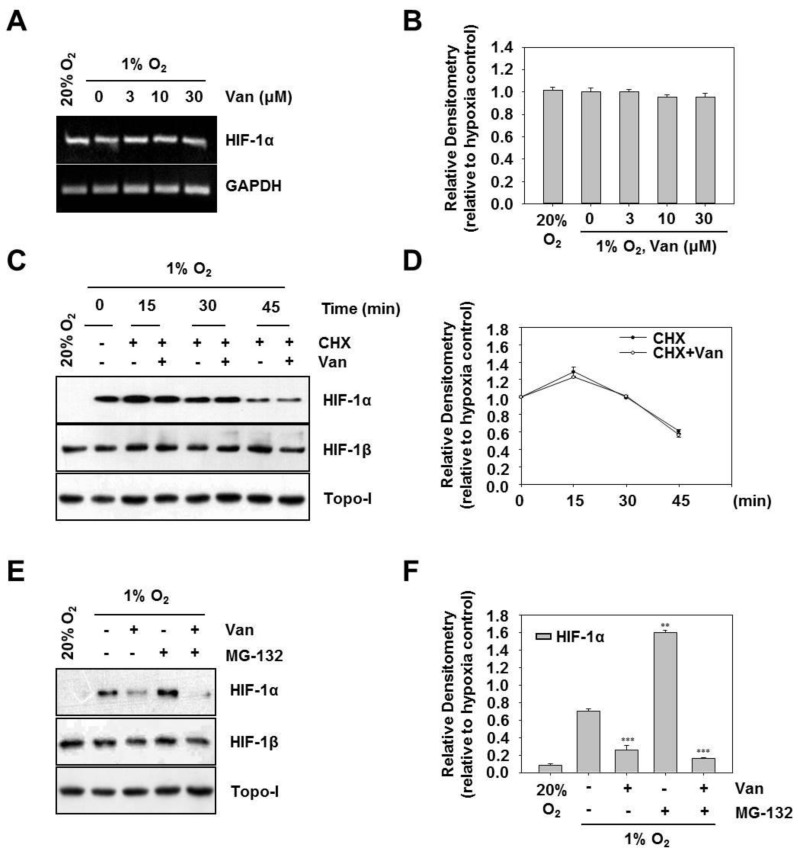
Figure 3.
Vanillic acid (Van) inhibits the protein synthesis of HIF-1α but not its degradation. (A) HCT116 cells were pretreated without or with indicated concentration of vanillic acid (Van), then cultured under normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 12 h. Total RNA was analyzed by RT-PCR as described in “Materials and Methods”. (B) Data were shown as mean ± SD (n = 3). (C) HCT116 cells were first treated under hypoxia for 4 h. Then cells were incubated in the presence of cycloheximide (CHX, 10 µM) and vanillic acid (Van, 30 µM). After 15, 30, or 45 min following the addition of cycloheximide (CHX), the whole-cell lysates for HIF-1β and nuclear extract for HIF-1α was detected by Western blot. Anti-Topo-I antibody was used as a loading control. (D) Data were shown as mean ± SD (n = 3). (E) HCT116 cells were cultured with proteasome inhibitor MG-132 (10 µM) for 30 min and treated with vanillic acid (Van, 30 µM). Then cells were transferred to hypoxia condition. The whole-cell lysates for HIF-1β and nuclear extract for HIF-1α was detected by Western blot. Anti-Topo-I antibody was used as a loading control. (F) Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 3). ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, compared with hypoxia control.