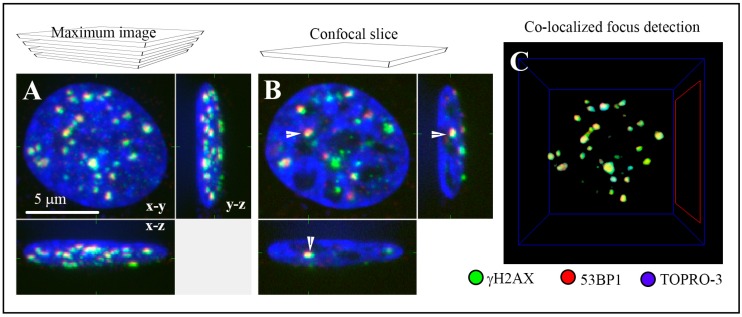
Figure 1.
The ability of immunofluorescence confocal microscopy to quantify DSBs (Double Strand Breaks) in cells incubated with nanoparticles or incubated with nanoparticles and consecutively irradiated. DSBs were quantified by the means of immunofluorescence detection of co-localized γH2AX (green) and 53BP1 (red) repair foci, the DSB markers. The nucleus of an illustrative U87 cell exposed to 2 Gy of γ-rays and spatially (three-dimensionally = 3D) fixed at 2 h post-irradiation (PI) is shown as: (A) a maximum intensity projection of 40 confocal slices (0.3 µm thick; “maximum image”) or (B) a single confocal slice (0.3 µm thick) intersecting the indicated (white arrow) γH2AX/53BP1 focus. Images are displayed in all three (in the x-y, x-z and y-z) planes, and chromatin is counterstained with TO-PRO-3 (artificially blue). (C) An example of computational detection of co-localized (yellow) γH2AX (green) and 53BP1 (red) repair foci in 3D space (Aquarium Software).