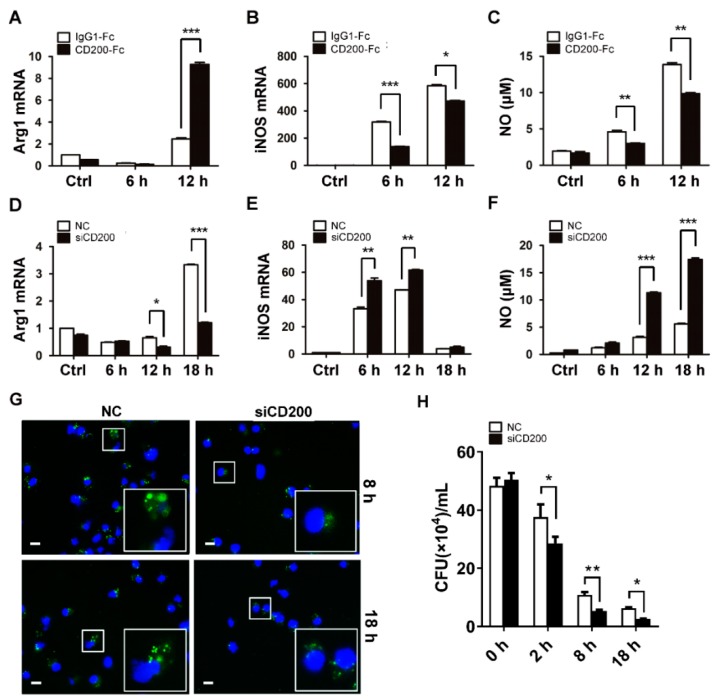
Figure 4.
CD200 signaling inhibits NO synthesis and bactericidal activity of S. aureus-infected macrophages. (A–C) Mouse BMDMs were pre-treated with CD200-Fc (2 μg/mL) or IgG1-Fc (2 μg/mL) for 1 h, and then stimulated with S. aureus (MOI = 1) for indicated time periods (0–12 h). Relative mRNA levels of Arg1 (A) or iNOS (B) were detected by qPCR. NO release was determined using Griess reagent system (C). (D–F) Mouse PEMs were transfected with siCD200 or NC siRNA for 48 h, and then stimulated with S. aureus (MOI = 1) for indicated time periods (0–18 h). Arg1 (D) and iNOS (E) mRNA levels and NO release (F) were determined. (G) PEMs transfected with siCD200 or NC siRNA were challenged with CFSE-labeled S. aureus (MOI = 10) for indicated time periods (0–18 h). Cells were collected, fixed, and stained with DAPI. Intracellular bacterial were observed using a fluorescence microscope. A partially enlarged view was shown in the lower left corner. Scale bars: 10 µm. Shown are representative images from three independent experiments. (H) Mouse PEMs were transfected with siCD200 or NC siRNA for 48 h, and then challenged with S. aureus (MOI = 10) for indicated time periods (0–18 h). Cells were lysed and the intracellular bacterial burden was determined by CFU counting. Results are expressed as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005.