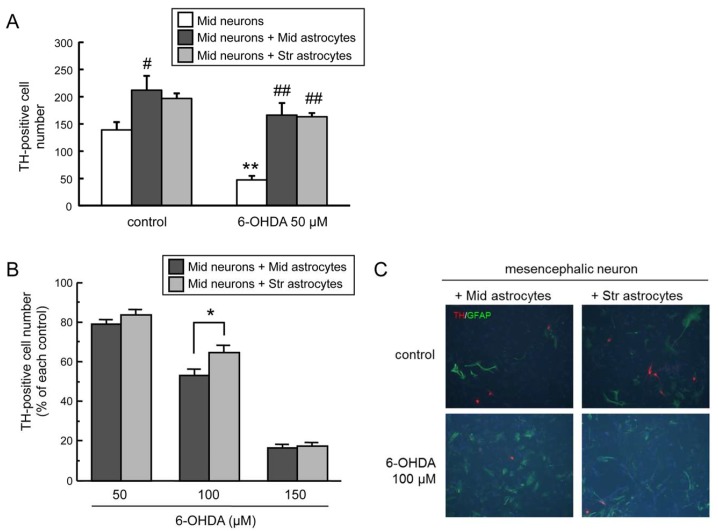
Figure 1.
(A) Neuroprotective effects of co-culture with mesencephalic or striatal astrocytes against 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced toxicity in mesencephalic neurons. Mesencephalic neurons were exposed to 6-OHDA (50 µM) for 24 h co-existing with mesencephalic or striatal astrocytes. Each value is mean of the number of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-positive neurons ± SEM (n = 4); ** p < 0.01 vs. each control group, # p < 0.05; ## p < 0.01 vs. each neuron group. (B) Regional difference in astroglial neuroprotective effect. Cell viability of TH-positive DA neurons co-cultured with mesencephalic or striatal astrocytes treated with 6-OHDA (50–150 µM) for 24 h. Data are means ± SEM (n = 4) expressed as percentage of each control group; * p < 0.05 between indicated two groups. (C) Representative fluorescence photomicrographs of TH (red) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (green) double immunostaining of mesencephalic neurons co-cultured with mesencephalic or striatal astrocytes treated with 6-OHDA (100 µM) for 24 h. Images are taken at 200× magnification.