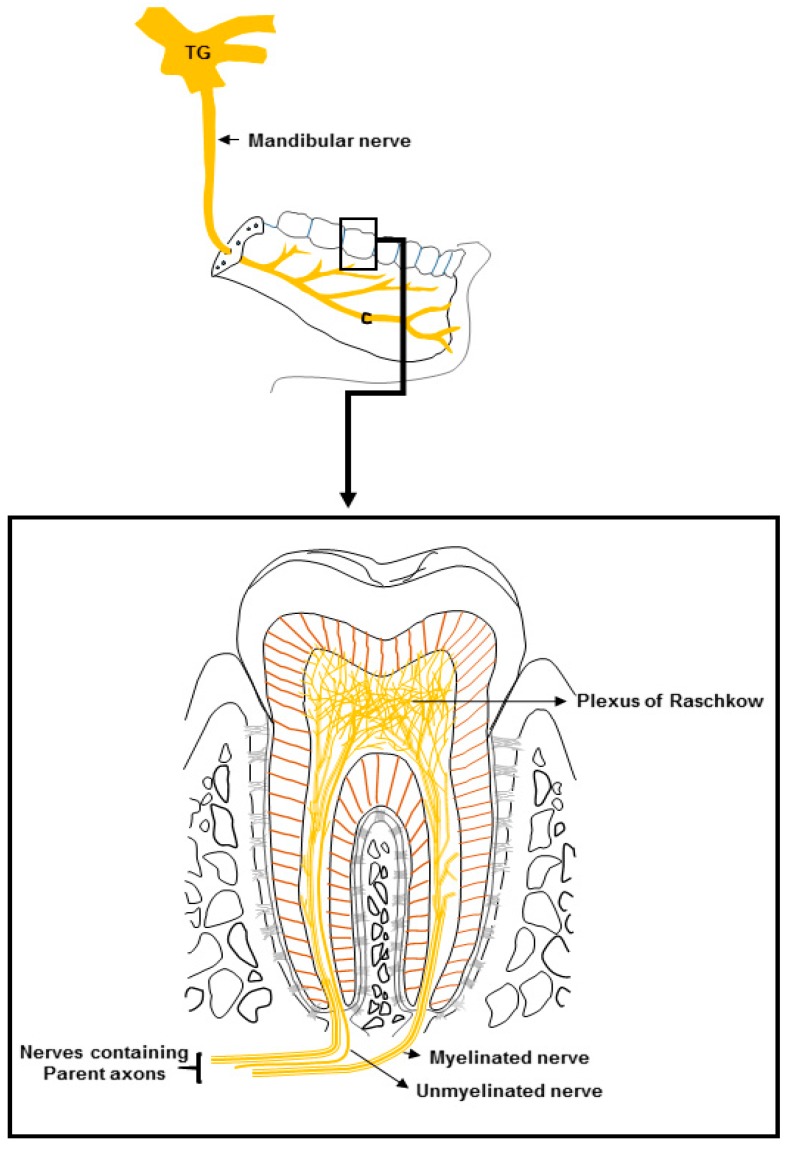
Figure 1.
Innervation of a tooth. The cell bodies of the dental primary afferent neurons are located in the trigeminal ganglion (TG). The axons of the afferent neurons project to the dental pulp through the two major branches of the trigeminal nerve, namely, the mandibular (shown in the figure) and maxillary nerves. A large number of the parent axons of the afferent neurons before entering into the dental pulp are myelinated. After entering the dental pulp, they extend branches and gradually lose their myelin sheath. In the crown area, the axons branch extensively to form the plexus of Raschkow. Many axons terminate very close to the odontoblasts and sub-odontoblastic cells, and some enter the dentinal tubules for a short distance into the inner part of the dentine.