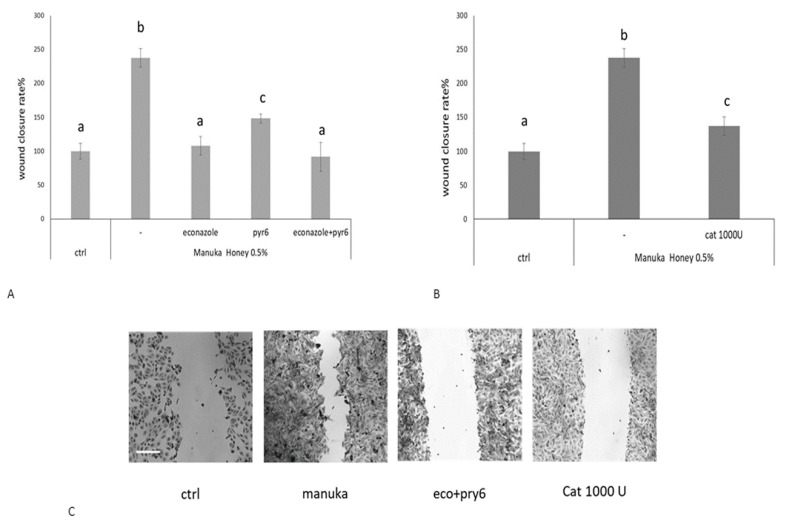
Figure 6.
Manuka honey-induced wound closure requires hydrogen peroxide and extracellular Ca2+ entry. (A) Effect of different inhibitors on honey-induced scratch wound repair of HaCaT monolayers. Each inhibitor was used according to the procedures, which were previously shown to inhibit manuka honey-induced extracellular Ca2+ entry: 10 μM Econazole, 1 μM Pyr6. We also used (B) 1000 U CAT. Wound closure rate is expressed as the difference between wound width at 0 and 24 h. Data were recorded 24 h after scratch wound healing of cells exposed to 0.5% manuka honey, in the presence or absence of various inhibitors. Bars represent mean ± SEM of wound closure inhibition deriving from two independent experiments, each with n = 20. For each inhibitor, different letters above bars indicate significant differences according to Tukey’s test (p < 0.01). (C) Micrographs of scratch wounded HaCaT monolayers incubated under control conditions or in the presence of manuka honey and inhibitors and then stained with blue toluidine and observed 24 h after wounding. Scale bar, 200 μm.