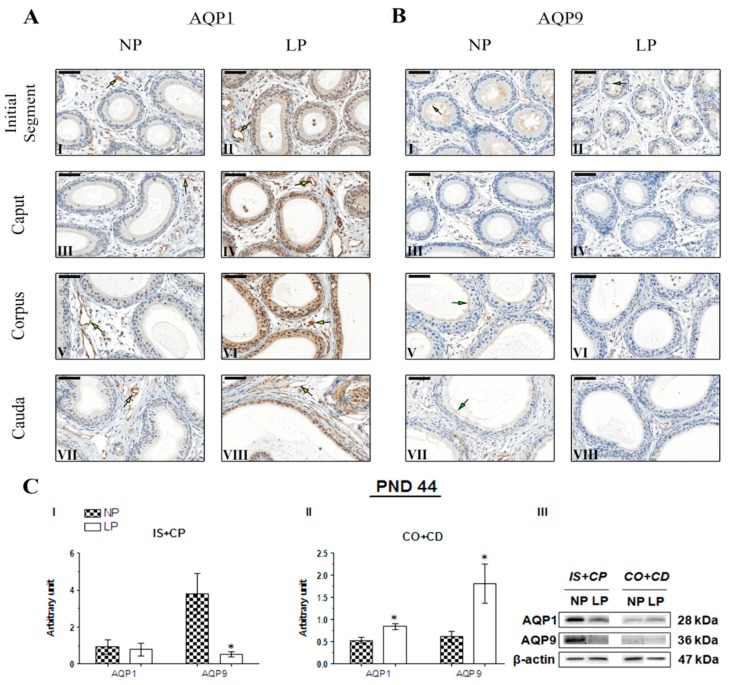
Figure 5.
Expression and immunolocalization of AQP1 and AQP9 in the epididymis of 44-day-old animals. (A) Immunoreactivity for AQP1 in endothelial cells of vascular channels in the initial segment (I and II), caput (III and IV), corpus (V and VI) and cauda (VII and VIII) of NP and LP animals (yellow arrows). (B) Immunoreactivity for AQP9 in the stereocilia of epididymis principal cells in the initial segment (I and II), caput (III and IV), corpus (V and VI) and cauda (VII and VIII) of NP and LP animals (green arrows). Bar = 50 µm. (C) Extracts obtained from individual animals were used for a densitometry analysis of the levels of the proteins in the initial segment plus caput (I) and corpus plus cauda (II) following normalization to the housekeeping protein β-actin. Representative blots showing the levels of the AQP1, AQP9 and β-actin proteins (III, right panel). Data are presented as means ± S.E.M. * p < 0.05, Mann-Whitney test.