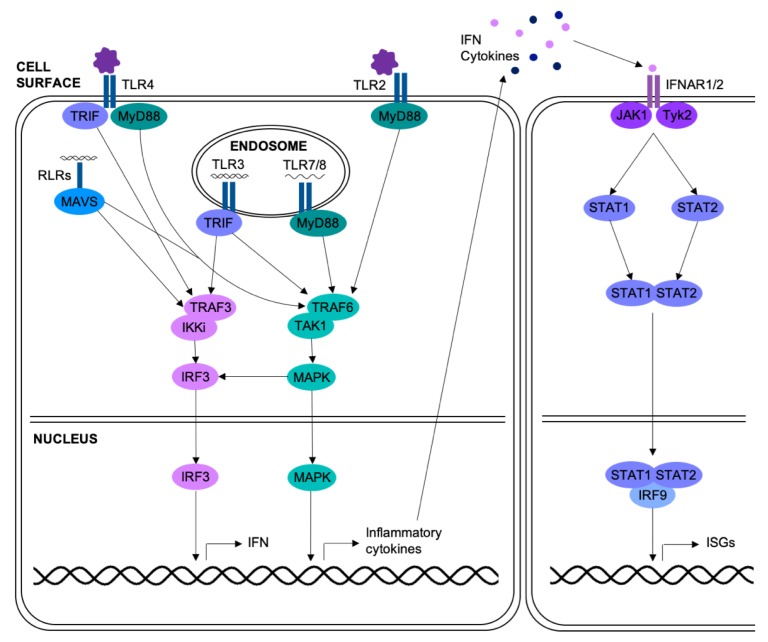
Figure 1.
Activation of signaling pathways in respiratory epithelial cells upon viral infection. PRRs detect viral infection of the cell: TLRs 2 and 4 can bind components of the viral surface, TLR3 binds dsRNA, TLR7/8 bind ssRNA, and the RLRs bind dsRNA or 5′-triphosphorylated ssRNA. Adaptor proteins MyD88, TRIF, and MAVS mediate the activation of signaling pathways, including the MAPK pathways. The MAPKs translocate into the nucleus where they activate transcription factors, leading to the transcription of genes for inflammatory cytokines. TRIF and MAVS signaling activates IRF3, leading to interferon production. The MAPK pathways can also activate IRF3. Inflammatory cytokines and interferons are released by the cell and act upon surrounding cells. IFN binds to the IFN receptor complex IFNAR1/2, activating the JAK/STAT pathway. JAK1 and Tyk2 phosphorylate STAT1 and STAT2 which dimerize, translocate to the nucleus and bind IRF9, forming ISGF3, which induces transcription of interferon stimulated genes (ISGs).