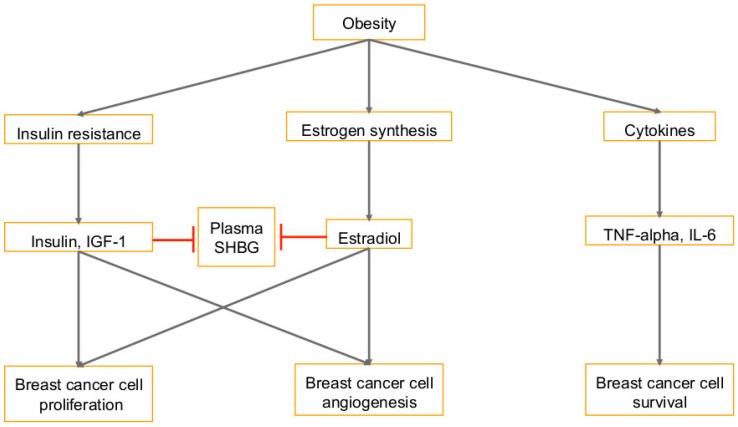
Figure 1.
Pathways that link breast cancer with obesity: Several consequences of obesity, such as insulin resistance, higher levels of circulating estrogen, and secreted cytokines play a role in the development of breast cancer. Insulin and IGF-1 promote proliferation and angiogenesis by activating the PI3K/Akt and Ras/Raf/MAPK pathways. Insulin also inhibits sex-hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), which binds testosterone and estradiol so there is increased free estradiol. Circulating estrogens promote growth of breast epithelial cells and lead to more proliferation and angiogenesis as well. Adipocytes can secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines which stimulate more lipolysis and further release of free fatty acids to promote cancer cell survival. T-bars in red denote inhibition.