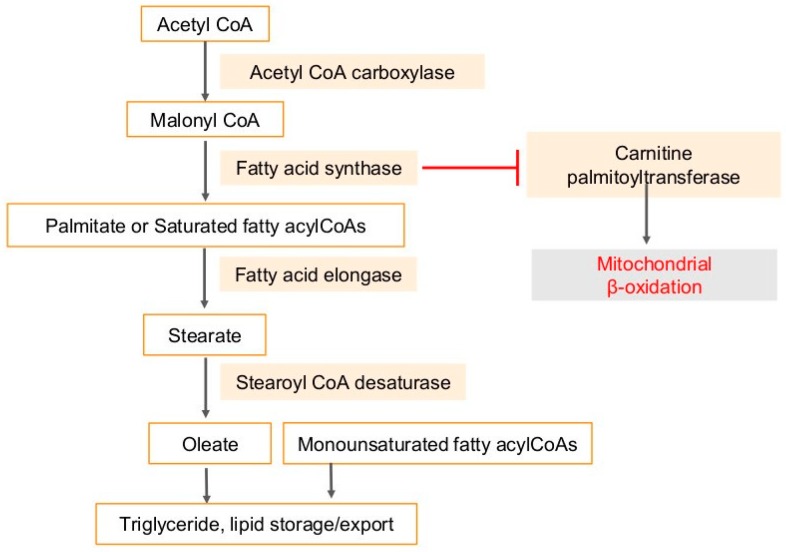
Figure 4.
Triacylglycerols are synthesized from acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-coA is metabolized to malonyl-CoA via acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which in turn is converted to Palmitate, the principal product of the fatty acid synthase system in animal cells. Palmitate is lengthened to form stearate by enzyme fatty acid elongase. Stearate, a saturated fatty acid is subsequently metabolized by stearoyl-CoA desaturase enzyme, that forms a double bond in stearoyl-CoA, leading to the monounsaturated fatty acid oleic acid. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT), the enzyme in the outer mitochondrial membrane, converts long-chain acyl-CoA species to their corresponding long-chain acyl-carnitines for transport into the mitochondria. CPT induces mitochondrial β-oxidation, which is a complex pathway involving energy metabolism. FASN inhibits CPT with resultant inhibition of fatty acid oxidation. T-bar in red denotes inhibition.