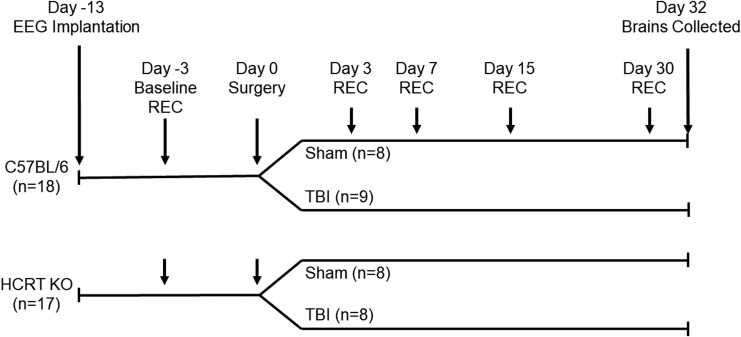
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of the protocols used in the present study. C57BL/6J and hypocretin knockout (HCRT KO) mice were implanted with electroencephalography (EEG) recording electrodes and allowed to recover. Forty-eight hours baseline EEG recordings were obtained from undisturbed mice, after which two mice were dropped from the study due to poor EEG signals. Mice of each genotype were randomized into either control (sham surgeries) or experimental (moderate traumatic brain injury [TBI] surgeries) groups. Moderate TBI was induced using controlled cortical impact with a piston depth of 1.0 mm. Forty-eight–hour recordings were obtained from all mice at 3, 7, 15, and 30 days post-surgery. After the last recording period (32 days post-surgery), animals were perfused and brains were removed for immunohistochemistry.