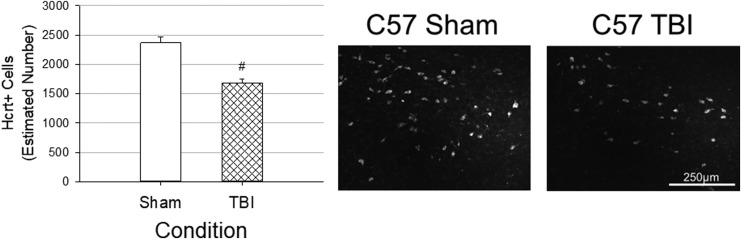
FIG. 7.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) reduces numbers of hypocretin neurons in C57BL/6J mice. Numbers of hypocretin neurons in the lateral hypothalamus ipsilateral to the injury site were estimated using unbiased stereology and the optical fractionator method. Values are means ± standard error of the mean obtained from C57BL/6J mice with sham surgery (n = 8) or TBI (n = 9). Counts were obtained at the end of the study, 32 days post-surgery. # indicates a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) between conditions (sham vs. TBI). Representative immunofluorescent images of the lateral hypothalamus ipsilateral to the injury site are presented.