Figure 2: CA3 is necessary for normal place field responses in CA1.
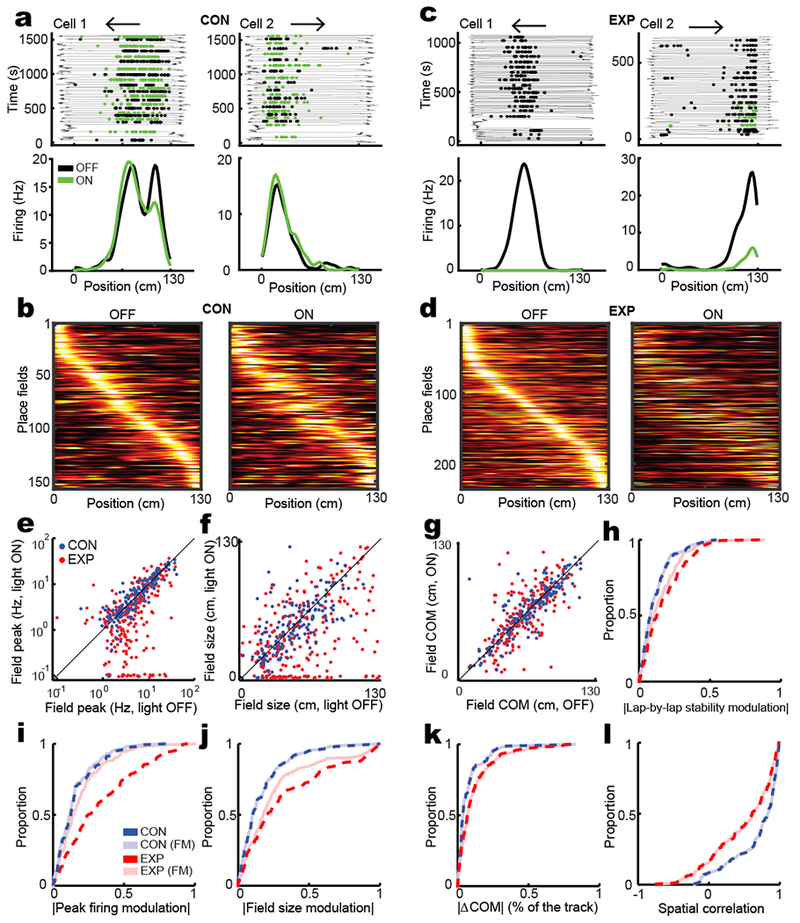
a) Two example CA1 place fields in CON rats. Top: Rat position as a function of time during linear track traversals (thin line), overlaid with spiking activity only in the running direction depicted by the arrow. Spikes in light OFF and light ON conditions are shown as black and green dots, respectively. Bottom: The average place fields calculated from above lap-by-lap spiking activities. b) All non-repetitive CON place fields sorted by their peak firing position during light OFF condition on the linear track. Each row depicts the color map of same place field in light OFF (left) and light ON (right) conditions. Each field is normalized by its maximum peak firing rate across OFF and ON conditions and the order of fields is similar between the two light conditions. c-d) Two example CA1 place field (c) and all non-repetitive sorted fields from EXP rats (d) as described in a-b. e-g) Place field features in light ON vs. light OFF conditions. Values are presented as mean ± s.e.m. e) Peak firing rate (CON: OFF: 7.97 ± 0.62 Hz and ON: 7.95 ± 0.55, two-tailed signed rank test, n = 157 fields, z(156) = −1.1, p = 0.3; EXP: OFF: 6.63 ± 0.43 and ON: 4.70 ± 0.40, two-tailed signed rank test, n = 236 fields, z(235) = 5.8, p = 10−8). f) Place field size (CON: OFF: 51.40 ± 1.95 cm and ON: 51.01 ± 1.98, two-tailed paired t-test, n = 157 fields, F(156) = 0.06, p = 0.80; EXP: OFF: 57.58 ± 2.17 and 39.97 ± 2.23; two-tailed signed rank test, n = 236 fields, z(235) = 6.8, p = 2×10−11). g) COM (CON: OFF: 65.81 ± 2.02 cm and 65.81 ± 2.03, two-tailed paired t-test, n = 156 fields, F(155) = 0.00, p = 1; EXP: OFF: 62.89 ± 1.54 and ON: 63.27 ± 1.81, two-tailed signed rank test, n = 207 fields, z(206) = −0.1, p = 0.9). h-l) the CDF of place field features in CON and EXP rats. h) The CDF of the absolute value of the lap-by-lap stability modulation of original and firing-matched (FM) place fields (Original: two-tailed rank sum test, n1 = 156 and n2 = 207 fields, z(362) = −3.9, p = 2×10−4; FM: two-tailed rank sum test, n1 = 156 and n2 = 207 fields, z(362) = −2.5, p = 0.013; EXP original vs EXP FM: two-tailed signed rank test, n = 207 fields, z(206) = 4.2, p = 5×10−5). i) The CDF of the absolute value of the amount of peak firing rate modulation (Original: two-tailed rank sum test, n1 = 156 and n2 = 207 fields, z(362) = −6.7, p = 3×10−11; FM: two-tailed rank sum test, n1 = 156 and n2 = 207 fields, z(362) = −2.1, p = 0.036). j) The CDF of the absolute value of the amount of field size modulation (Original: two-tailed rank sum test, n1 = 156 and n2 = 207 fields, z(362) = −5.1, p = 5×10−7; FM: two-tailed rank sum test, z(362) = −3.4, p = 7×10−4; EXP original vs EXP FM: two-tailed signed rank test, n = 207 fields, z(206) = 3.2, z(362) = −3.0, p = 0.0015). k) The CDF of the absolute value of the amount of COM shift (Original: two-tailed rank sum test, n1 = 156 and n2 = 207 fields, p = 0.0025; FM: two-tailed rank sum test, n1 = 156 and n2 = 207 fields, z(362) = −3.3, p = 0.001; EXP original vs EXP FM: two-tailed signed rank test, n = 207 fields, p = 0.3). l) The CDF of the spatial correlation (Original: two-tailed rank-sum test, n1 = 156 and n2 = 207 fields, z(362) = 5.0, p = 10−6; EXP original vs EXP FM: two-tailed signed rank test, n = 207 fields, z(206) = 2.7, p = 0.008).
