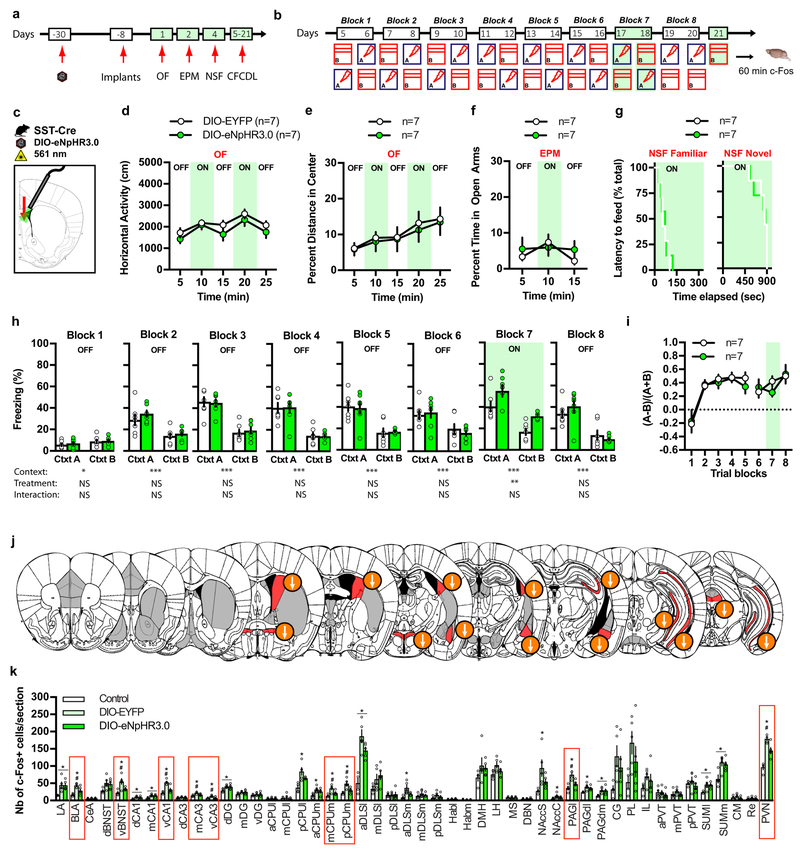
Figure 4. Optogenetic silencing of DLS SST-INs increases contextual fear responses.
a-b) Schematic of behavioral testing timeline. c) Schematic illustrating infection of SST DLS-INs with DIO-eNpHR3.0 and fiber optic implantation on top of DLS in SST-Cre mice. d-g) Silencing SST cell bodies in DLS (constant illumination) has no effect on locomotor behavior and innate anxiety in OF (d-e) and EPM (f) and novelty suppressed feeding (NSF) (g). Means ± SEM; n= 7, 7 mice per group, mixed factor two-way ANOVA. h) Silencing SST cell bodies (constant illumination) increases freezing behavior in context A and B on block training 7. Means ± SEM; n= 7, 7 mice per group, mixed factor two-way ANOVA (repeated measure over time) followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons post-hoc test. i) Silencing SST cell bodies (constant illumination) did not alter fear discrimination ratio. Means ± SEM; n= 7, 7 mice per group, mixed factor two-way ANOVA (repeated measure over time). j) Schematic representation of the effect of light silencing of SST cell bodies in DLS on brain-wide c-Fos expression 60 min following exposure to context B (day 21). Regions highlighted in red denote a significant effect of DIO-eNpHR3.0 and arrows indicate the direction of the effect. k) Detailed c-Fos immunostaining quantifications. Brain regions highlighted with red boxes indicate a significant effect of DIO-eNpHR3.0. Means ± SEM; n= 4, 5, 5 mice per group, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons post-hoc test. *p < 0.05, DIO-EYFP or DIO-eNpHR3.0 versus controls, #p < 0.05, DIO-EYFP versus DIO-eNpHR3.0. All statistics detailed in Supplementary Table 1.