FIGURE 1.
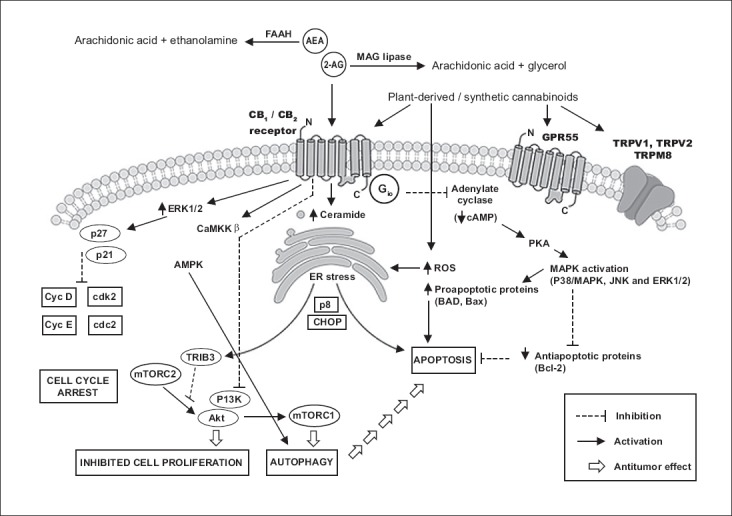
Example of different signaling pathways induced by cannabinoids in cancer cells [46,51,53-55]. By targeting the endocannabinoid system (ECS), cannabinoids affect many essential cellular processes and signaling pathways which are crucial for tumor development. For example, they can induce cell cycle arrest, promote apoptosis, and inhibit proliferation, migration and angiogenesis in tumor cells. AEA: Anandamide; 2-AG: 2-Arachidonoylglycerol; Akt: Protein Kinase B; AMPK: 5’ adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; Bad: Bcl-2-associated death promoter; Bax: Apoptosis regulator; CaMKK: Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase; Cdk 2: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2; CHOP: C/EBP homologous protein; CycD: Cyclin D; Cyc E: Cyclin E; ELK1: ETS domain-containing protein; ERK: Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; FAAH: Fatty acid amide hydrolase; GPR55: Orphan G-protein coupled receptor 55; MAG lipase: Monoacylglycerol lipase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; p8: Candidate of metastasis 1; p21: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1; p27: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PKA: Protein kinase A; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TRPV1: Transient receptor potential vanilloid receptor 1; TRPV2: Transient receptor potential vanilloid receptor 2; TRPM8: Transient receptor potential melastatin 8; mTORC1: Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; mTORC2: Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2; TRIB3: Tribbles homolog 3.
