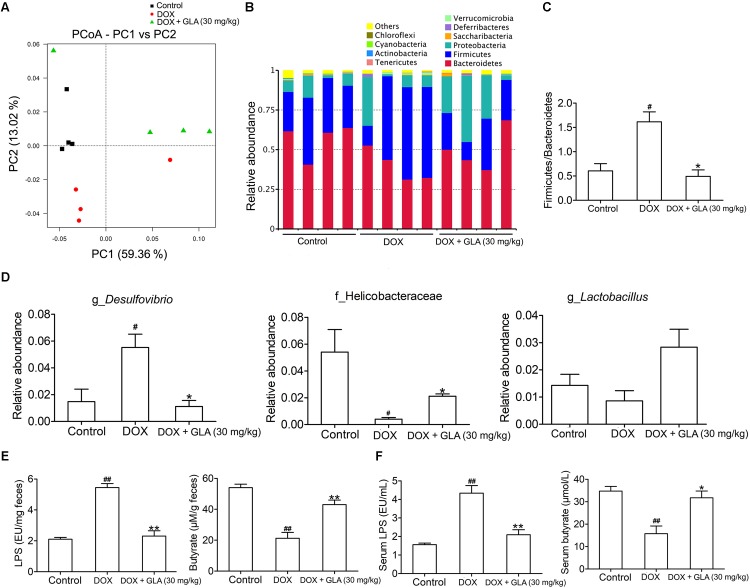
FIGURE 2.
Glabridin (GLA) prevents doxorubicin (DOX)-induced dysbiosis of gut microbiota in mice. A single dose of DOX (20 mg/kg) was intraperitoneally injected into the C57BL/6 mice to induce acute cardiotoxicity. GLA (30 mg/kg) or vehicle was intragastrically administered once daily for 12 days, starting 7 days before DOX injection. (A) Principal co-ordinates analysis plot of bacterial β-diversity (n = 4). (B) The relative taxonomic abundance at the phylum level of gut microbiota (n = 4). (C) The ratios of Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes (n = 4). (D) The relative abundance of Desulfovibrio genus, helicobacteraceae family and Lactobacillus genus (n = 4). (E,F) Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and butyrate levels in feces and peripheral blood were determined by Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL) assays or high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), respectively (n = 10). The values are presented as the mean ± SEM. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. control, ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 vs. DOX.