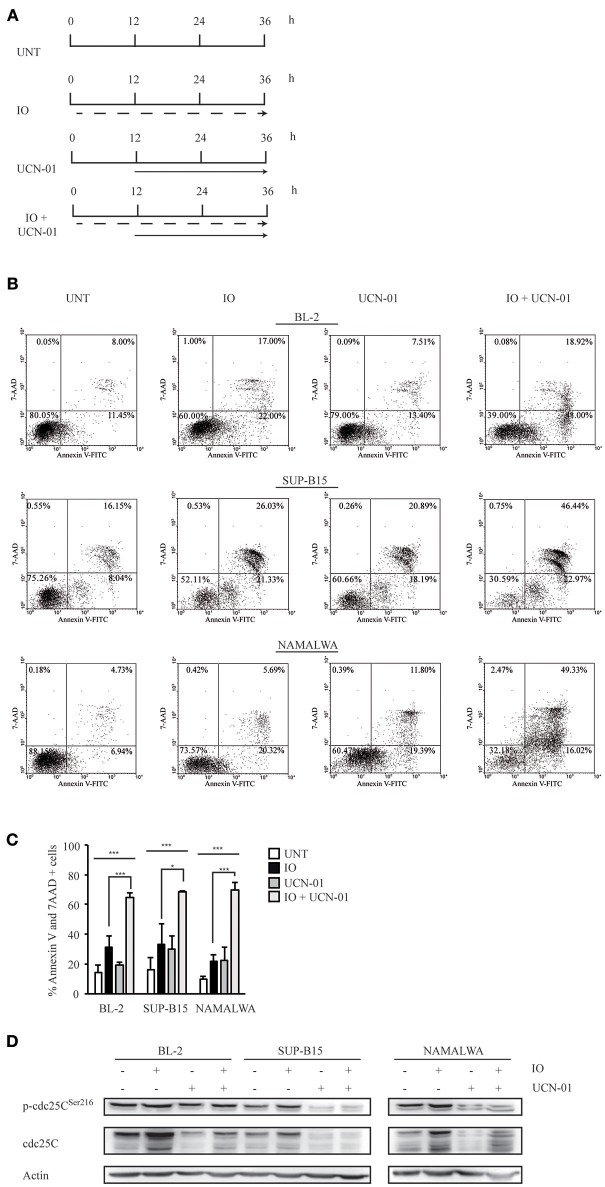
Figure 4.
Treatment with Inotuzumab Ozogamicin and UCN-01 determines an increase in the apoptotic rate of CD22-positive cells. (A) Treatment scheme employed in the experiments described in panels (B–D). BL-2, SUP-B15 and Namalwa cell lines were either left untreated (UNT) or were exposed to IO (dashed arrow) according to their respective IC50 values, to 100 nM UCN-01 (solid arrow) or to a combination of the two drugs. In the latter case cell lines were kept for 12 h in IO and UCN-01 was added for the remaining 24 h of the experiment. (B) Representative experiment displaying the apoptotic rates detected in BL-2, SUP-B15 and Namalwa cell lines. The indicated cells were grown in the absence of drugs or treated with IO or UCN-01. Apoptosis was then evaluated after Annexin V-FITC/7AAD double staining. The indicated percentages show the distribution of necrotic, early and late apoptotic cells after IO and UCN-01 treatment, alone or in combination. (C) Histograms representing the average percentage of Annexin V and 7 AAD-positive cells in the untreated condition or after exposure to IO, UCN-01 or a combination of the two drugs. Columns represent average ± standard deviation of three independent experiments performed in triplicates. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 (D) Cell lines treated, as specified in (A), were also harvested, lysed and probed with the specified antibodies to perform immunoblot assays. Actin was used as a loading control. The depicted blots are representative of three separate experiments.