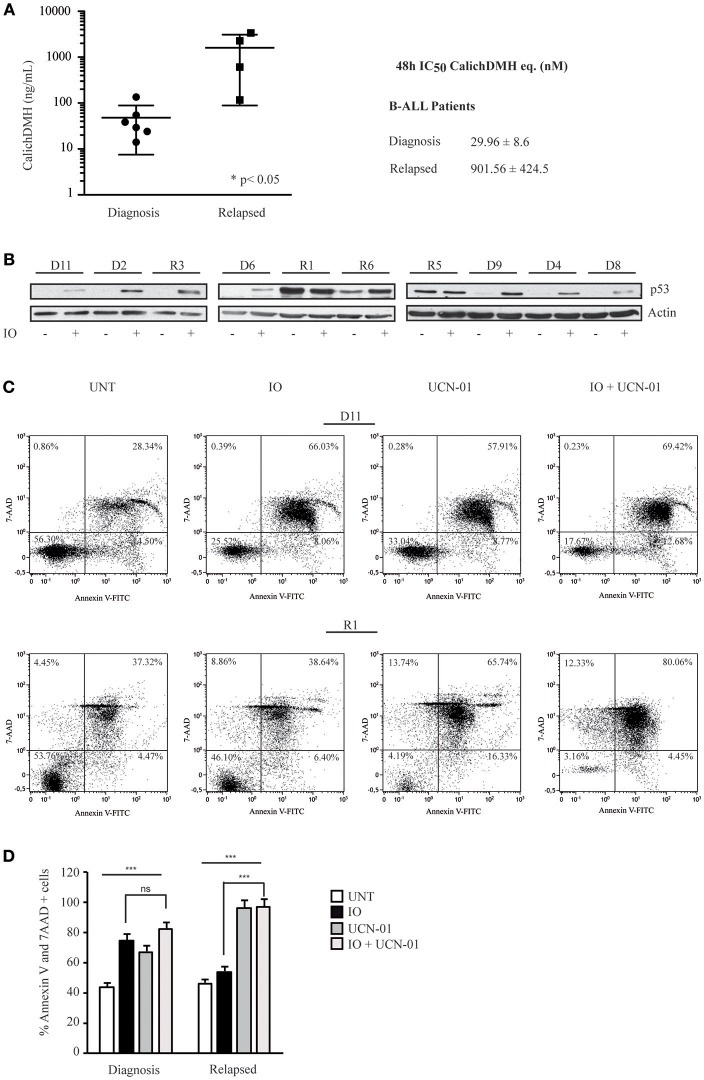
Figure 7.
Primary human CD22-positive cells expressing wild-type p53 display high sensitivity to Inotuzumab Ozogamicin. (A) Reduction in cell viability calculated on mononuclear cells derived from six CD22-positive human B-ALL patients at diagnosis and four patients with r/r B-ALL. After a 48 h incubation with increasing IO concentrations, the reduction of cell proliferation was evaluated employing the ATPLite luminescence assay. The right panel indicates average ± standard deviation of the IC50 values, expressed as nM equivalents of CalichDMH. (B) The indicated primary cells derived from B-ALL patients at diagnosis (D) or from r/r B-ALL (R) were also treated for 48 h with calicheamicin equivalents corresponding to their IO IC50 average values. Lysates from these cells were then blotted using the specified antibodies. Actin was used as a loading control. (C) Primary cells, derived from one B-ALL (D11) and one r/r B-ALL (R1) patient, were left untreated or exposed to the IO IC50 average value for B-ALL patients at diagnosis (29.96 nM) and UCN-01 100 nM, alone or in combination, employing the scheme described in Figure 4A. Apoptosis was then evaluated after Annexin V-FITC/7AAD double staining. The indicated percentage values show the distribution of necrotic, early and late apoptotic cells. (D) Histograms representing the average percentage of Annexin V and 7 AAD positive cells in the untreated condition or after exposure to IO, UCN-01 or a combination of the two drugs. Columns represent average ± standard deviation of two independent experiments. ***p < 0.001; ns, not significant.