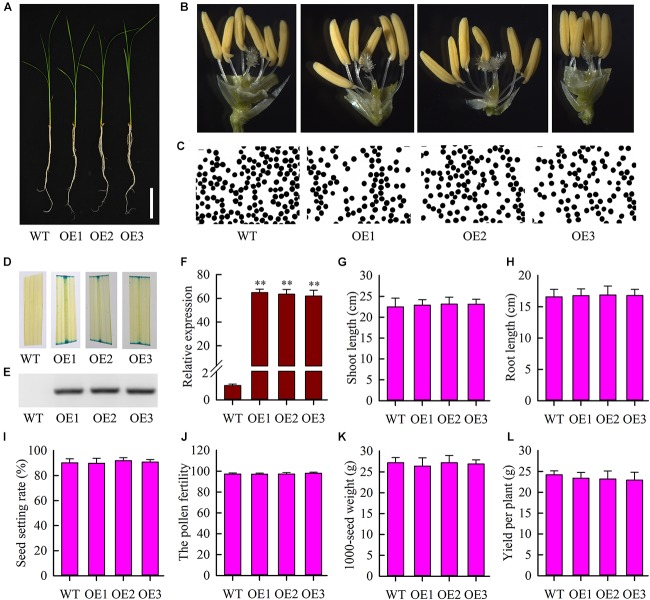
FIGURE 4.
Phenotype of wild-type plants and transgenic plants with OsMYB6. (A) Phenotype of transgenic plants with OsMYB6 and wild-type plants. Twelve-day-old seedlings cultured in Yoshida’s culture solution were photographed. Bar = 5 cm. (B) Flower structure analysis of the wild-type, OE1, OE2, and OE3 plants. (C) Pollen germination of the wild-type and transgenic plants. (D) GUS staining analysis in leaves from the wild-type, OE1, OE2, and OE3 plants. In addition, the pCAMBIA1301 vector contained a β-glucuronidase (GUS) gene under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter. (E) PCR analysis of the regenerated plants using gene specific primers of hygromycin gene. (F) qRT-PCR analysis of OsMYB6 expression in the transgenic lines with OsMYB6 and wild-type plants. OE1, OE2, and OE3 are three individual transgenic plants overexpressing OsMYB6 gene. (G) Shoot length in transgenic plants overexpressing OsMYB6 and wild-type plants after 12 days of growth on Yoshida’s culture solution. (H) Root length in transgenic plants overexpressing OsMYB6 and wild-type plants after 12 days of growth on Yoshida’s culture solution. (I) Seed setting rate among the wild-type, OE1, OE2, and OE3 plants. (J) The pollen fertility from the wild-type, OE1, OE2, and OE3 plants. (K) 1000-grain weight comparison of the seeds from the wild-type, OE1, OE2 and OE3 plants. (L) Yield per plant among the wild-type, OE1, OE2, and OE3 plants. Values represent (G–L) means of n = 30 ± SD (Duncan test: ∗∗P < 0.01) from three independent biological experiments.