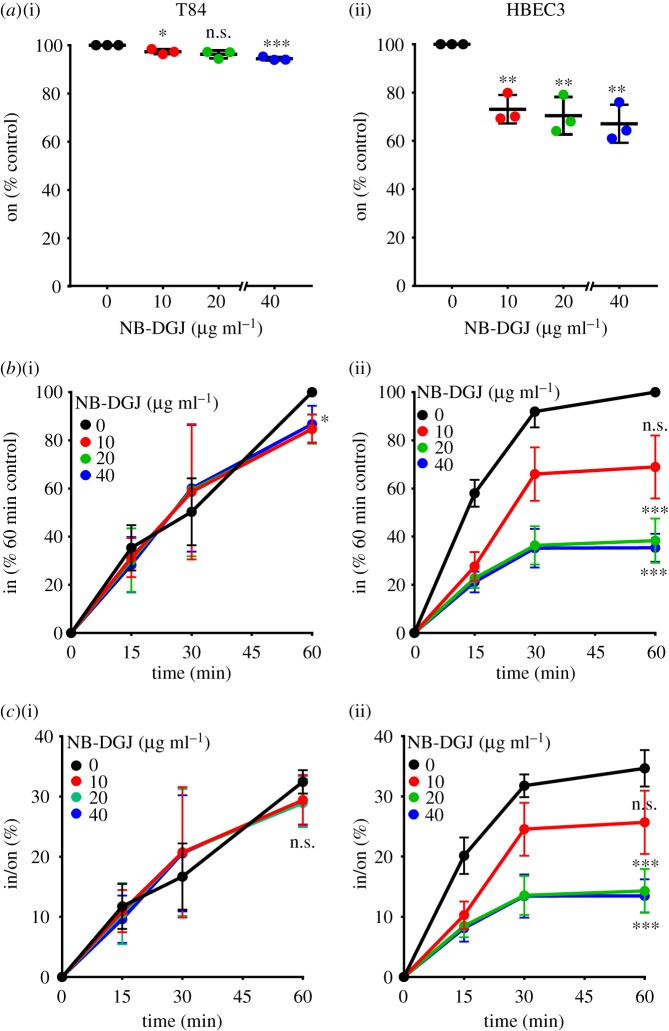
Figure 2.
Endogenous gangliosides are significant contributors to CTB cell surface binding and internalization in lung but not colonic epithelial cells. (a–c) T84 and HBEC3 cells were cultured with the indicated concentrations of NB-DGJ (in µg ml−1) for 3 days, then incubated with 4 µg ml−1 CTB on ice for 30 min. (a) To measure cell surface binding of CTB by on-cell ELISA, cells were maintained at 4°C. The raw values obtained were averaged, normalized to the untreated control and compared with the untreated control for statistical analysis. (b) To measure internalization of CTB by in-cell ELISA, cells were incubated at 37°C for the indicated times and normalized to the values obtained for the untreated control at the 60 min time point. For statistical comparisons, internalization values at the 60 min time point were compared with the untreated control. (c) The efficiency of CTB internalization in T84 and HBEC3 cells was calculated by the ratio of internalized CTB at each of the time points in an individual experiment to the corresponding CTB cell surface binding values obtained by on-cell ELISA. For all panels, data represent three independent experiments performed on different dates. Each experiment comprised the average of four samples. Statistical significance determined by comparing data obtained from the three experiments by the unpaired Welch test: *** indicates p < 0.001, ** indicates p < 0.01, * indicates p < 0.05. n.s. indicates difference from the untreated sample not statistically significant. (Online version in colour.)