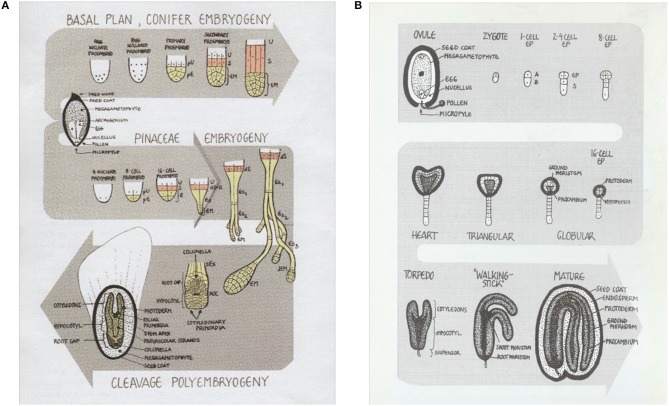
Figure 1.
Zygotic embryo development in gymnosperms and angiosperms differs in some major aspects. (A) Early stages of conifer embryo development. The conifer zygote results from a single fertilization event. At the beginning of embryogenesis, there are free nuclear stages followed by a pro-embryo stage. Main characteristics of conifer embryo development are the polyembryogenic features of some conifer species where the zygotic embryos to different degrees proceed through a process of embryo-cleavage that results in multiple embryos that are eventually eliminated by programmed cell death. (B) In angiosperm embryo development the sporophytic generation is initiated by a double fertilization event resulting in one embryo. (A) pU, primary upper tier; pE, primary embryonal tier; U, upper tier; S, suspensor tier; EM, embryo mass; dS, R: dysfunctional suspensor tier; Es, embryonal suspensor tier; dEM, degenerating embryo mass; ROC, root organization center; sEs, secondary embryonal suspensor cells. (B) A, apical cell; B, basal cell; EP, embryo proper; S, suspensor. Figure adapted from Egertsdotter (1996).