Fig. 2.
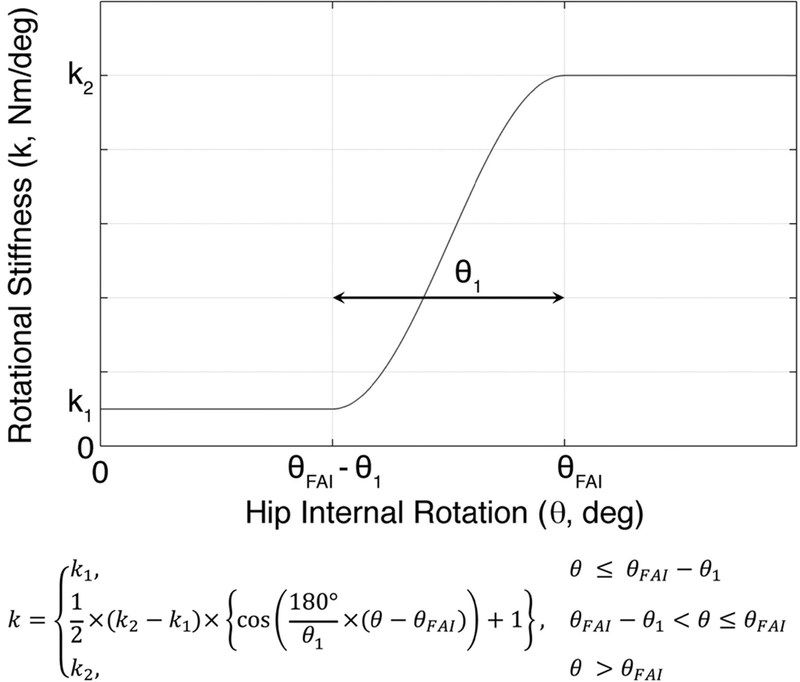
The axial hip rotational stiffness versus angular rotation relationship used to simulate femoracetabular impingement (FAI), where θ is the hip internal rotation angle; θFAI is the hip internal rotation angle at the end of the range of motion secondary to impingement; θ1 is the hip internal rotation angle where the impingement begins and is set to 5°; k1 is the stiffness coefficient when the impingement does not occur and is set to 0.5 Nm/deg; k2 is the stiffness coefficient when the hip internal rotation angle exceeds θFAI and is set to 5 Nm/deg
