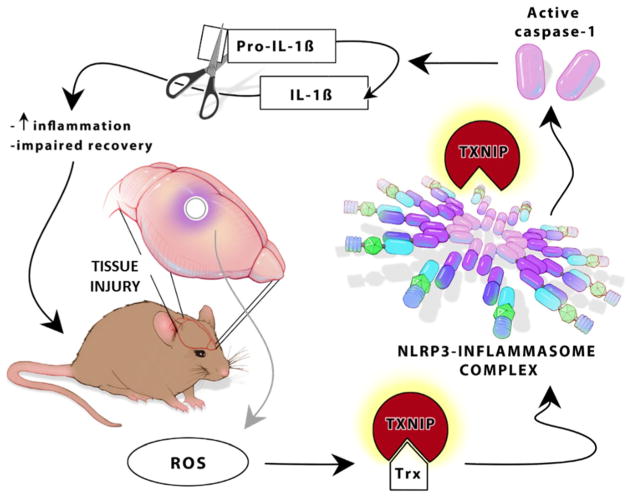
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of TXNIP as a direct NLRP3 activator. ROS generation is a common feature in several types of acute and chronic brain tissue injuries. ROS is well characterized to dissociate TXNIP from its endogenous ligand TRX. This leads to direct TXNIP attachment to NLRP3-inflammasome resulting in activation of caspase-1 that in turn causes maturation and cleavage of pro-IL-1β to IL-1β. This further ends with increased inflammation and impaired recovery after brain injury in mice. ROS, reactive oxygen species; TXNIP, thioredoxin-interacting protein; NLRP3, Nod-like receptor protein 3; IL-1β, interleukin-1-beta