Figure 1.
Resistance of VA-RCAZ to CAZ.
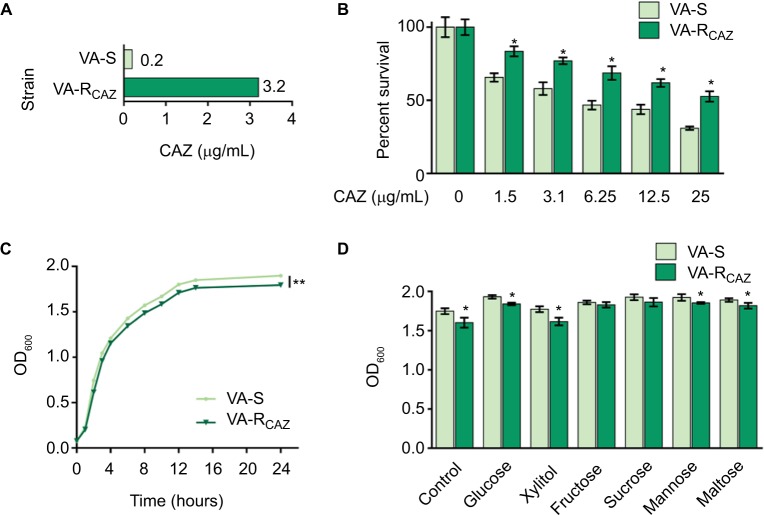
Notes: (A) MIC of CAZ in VA-S and VA-RCAZ. Logarithmic phase of VA-S and VA-R 5 CAZ (10 colony-forming units) were incubated with 3% NaCl LB broth containing CAZ ranging from 0.05 to 100 μg/mL in microwell plate at 30°C for 16 hours. (B) Percent survival of VA-S and VA-RCAZ vs concentration of CAZ. Overnight VA-S and VA-RCAZ were incubated with CAZ (0, 1.5, 3.1, 6.25, 12.5, and 25 μg/mL) in M9 minimal medium plus NaAc (10 mM) at 30°C for 6 hours. (C) Growth curve of VA-S and VA-RCAZ. Overnight VA-S and VA-RCAZ were diluted to 1:100 using fresh 3% NaCl LB medium and grown in the indicated periods. OD600 of the bacterial cultures was measured at the indicated time. (D) Growth ability of VA-S and VA-RCAZ in the presence of different carbon sources. Overnight VA-S and VA-RCAZ were diluted to 1:100 using fresh 3% NaCl LB medium and grown with glucose, xylitol, fructose, sucrose, mannose, or maltose at 30°C for 10 hours. OD600 of the bacterial cultures was measured. Results (B–D) are displayed as mean ± SEM, and significant differences are identified as determined by Student’s t-test. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. At least three biologic repeats were carried out.
Abbreviations: CAZ, ceftazidime; LB, Luria–Bertani; VA-RCAZ, ceftazidime-resistant Vibrio alginolyticus; VA-S, ceftazidime-sensitive Vibrio alginolyticus.