Figure 6.
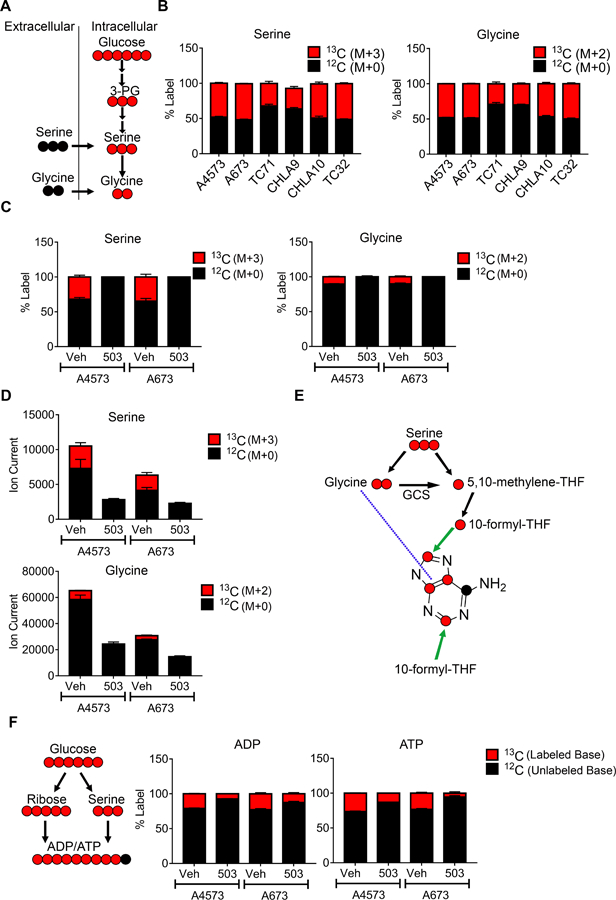
Effect of menin inhibition on de novo synthesis of serine and glycine. (A) Schematic depicting tracing of serine (M+3) and glycine (M+2) (both red) from 13C-labeled glucose via de novo synthesis. Unlabeled serine and glycine, in black, can be imported from the extracellular space. (B) Baseline fractional incorporation of 13C-labeled glucose into serine (M+3) and glycine (M+2) in a panel of Ewing sarcoma cell lines. (C) Fractional incorporation of 13C-labeled serine and glycine in vehicle- and MI-503 treated cells. (D) Total cellular pools of serine and glycine after MI-503 treatment. (E) Chemical structure of the adenine base, showing potential locations of glucose-derived, 13C-labeled serine and glycine carbon. GCS: glycine cleavage system. (F) Schematic and fractional incorporation of 13C-labeled glucose into ADP and ATP.
