FIGURE 1.
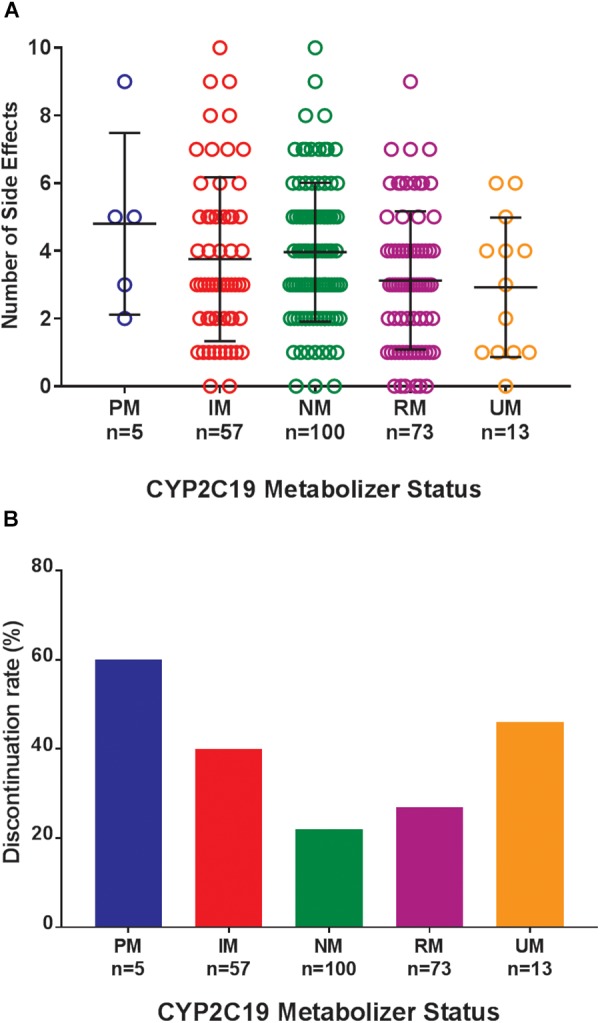
(A) Total number of side effects experienced during treatment with escitalopram or citalopram (es/citalopram) by 248 patients included in the tolerability analysis. CYP2C19 metabolizer status is associated with the total number of side effects experienced (p = 0.015). The association with CYP2C19 metabolizer status remained significant (p = 0.019) in a multivariate regression model that accounted for es/citalopram dose and concomitant medications. Mean and standard deviation are indicated by the bar and whiskers. (B) Discontinuation rates by CYP2C19 metabolizer status in the tolerability analysis with a documented reason for discontinuation of es/citalopram in the electronic medical record. PMs and IMs were significantly more likely to discontinue es/citalopram relative to NMs (p = 0.007, χ2), while RMs and UMs were not (p = 0.20, χ2). PM, poor metabolizer; IM, intermediate metabolizer; NM, normal metabolizer; RM, rapid metabolizer; UM, ultrarapid metabolizer; n, number.
