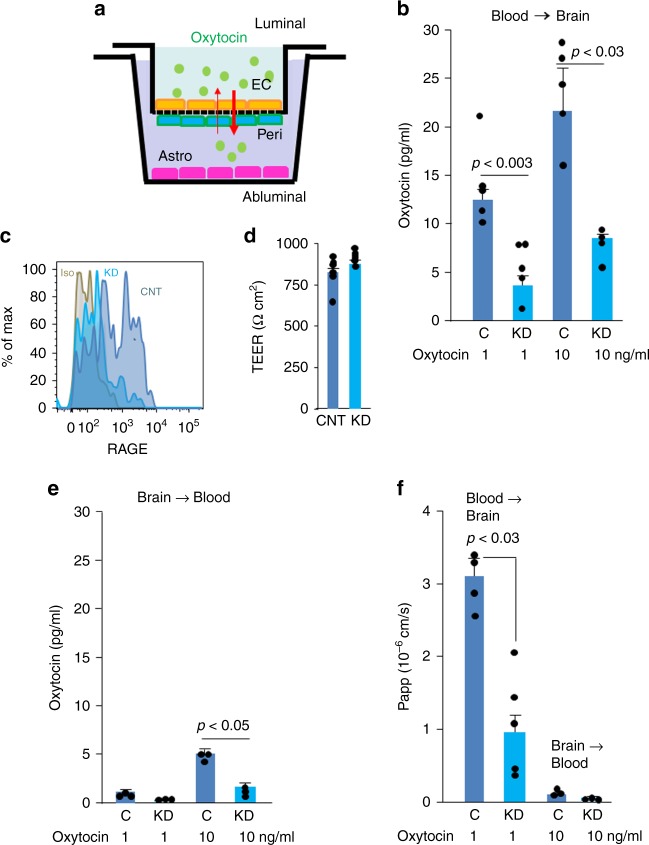
Fig. 2.
RAGE transports oxytocin across an in vitro blood brain barrier (BBB). a A schematic diagram of the monkey BBB kit (PharmaCo-Cell). EC, monkey brain capillary endothelial cells; Peri, rat brain pericytes; Astro, rat astrocytes. The upper and the lower chambers represent the luminal (blood) and abluminal (brain extracellular space) sides, respectively. b Oxytocin (1 or 10 ng/ml) was added to the upper (luminal, blood) chambers of the model BBB system, and 3 h later oxytocin was quantified in the lower (abluminal, brain) chambers (n = 4–5). c Flow cytometry. The endothelial cells used in the upper chamber in a were treated with RAGE shRNA (knockdown, KD) or control (C or CNT) vectors to assess the effects of RAGE knockdown. Isotype control (Iso) instead of anti-RAGE antibody assesses background signal. d Transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER, Ωcm2) measures >150 Ωcm2 indicate integrity of the model BBB (n = 6). e Conversely, oxytocin was added to the abluminal chambers and its transport to the luminal chamber was quantified (n = 3). f The apparent permeability constants (Papp) for transfer were calculated from the distribution ratios across the chambers (n = 3–5). Values are mean ± SEM