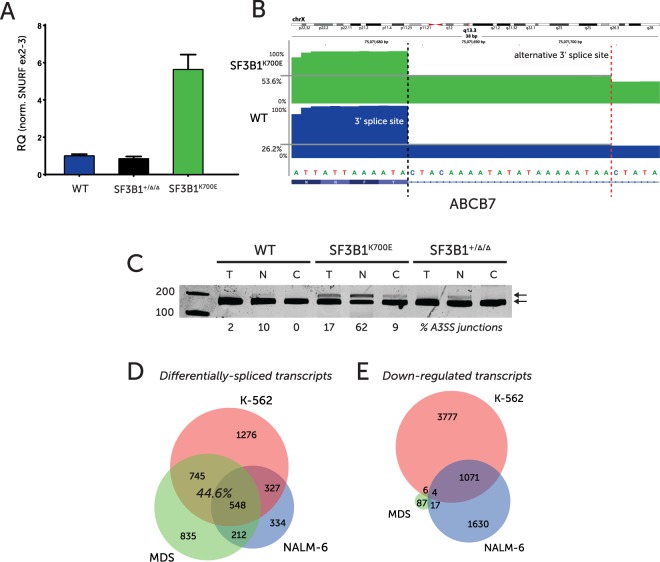
Figure 2.
(A) Relative quantities of SNURF exon 2b measured by qPCR across ex2-2b and normalized to ex2-3 levels. Error bars represent SEM. (B) RNA-Seq, total read count-normalized, coverage plots at the ABCB7 exon previously published as having an alternative 3′ splice site. Note: gene is on reverse strand. (C) RT-PCR of cDNA from wildtype, SF3B1K700E & SF3B1+/Δ/Δ whole cell (T), nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic fractions (C). Amplicon spans ABCB7 exons 8–9 (RefSeq NM_004299). Percentages represent RNA-seq reads that span the alternative 3′ splice site as a fraction of the total number of reads spanning exons 8 and 9. (D) Venn diagram representing overlap in genes identified as having altered splicing by dSpliceType (all types) in SF3B1K700E vs wildtype samples. Comparing RNA-Seq data from Darman et al. (NALM-6 cells, n = 3), Dolatshad et al. (primary MDS, n = 4) and this study (n = 2). (E) Venn diagram representing overlap in genes identified as downregulated at the transcript-level by DESeq. 2 analysis in SF3B1K700E vs wildtype samples. Comparing RNA-Seq data from Darman et al. (NALM-6 cells), Dolatshad et al. (primary MDS) and this study.