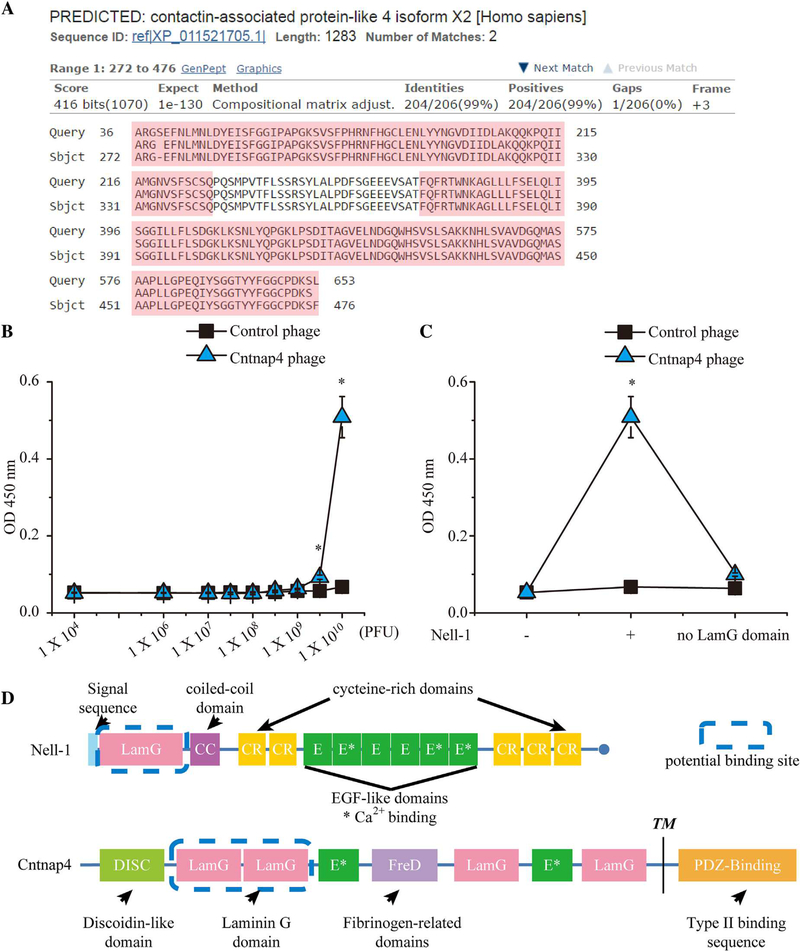
Fig. 1.
Confirmation of binding affinity between Cntnap4 phages and Nell-1 using a binding dissociation constant ELISA assay. (A) The Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) result of the amino acid sequence displayed by the T7 phage constructed with human brain cDNA matched the human Cntnap4 partial protein sequence. Query = the amino acid sequence enclosed by the T7 phage DNA; Sbjct = the matched amino acid sequence Cntnap4. The LamG domains are highlighted in pink. (B) By increasing the number of phages incubated with Nell-1 precoated ELISA plates, the Cntnap4 phage demonstrated significantly higher binding affinity than the control phage. (C) The Cntnap4 phage revealed high binding affinity only to full-length Nell-1 and not to LamG domain-deleted Nell-1. (D) Structures of Nell-1 and Cntnap4 and their potential interaction domains. Nell-1 is a secreted protein composed of 810 amino acids with a molecular weight of ~90 kDa before N-glycosylation and oligomerization. It contains several structural motifs including a laminin G (LamG) domain, a coiled-coil (CC) domain, five cysteine-rich (CR) domains, and six epidermal growth factor (E)-like domains. Cntnap4 is a transmembrane protein of 1310 amino acids consisting of a large extracellular domain, a single membrane-spanning domain, and a short cytoplasmic region at the carboxy-terminus. The extracellular region is composed of a discoidin-like domain (DISC), a fibrinogen-related domain (FreD), two E repeats, and four LamG domains. The cytoplasmic region contains a binding site for PDZ domains. The potential binding domain of Nell-1 and Cntnap4 is highlighted by the blue dashed line. TM= transmembrane. Mean ± SEM of six independent experiments performed in triplicate is shown. *p < 0.05 when compared with control phage.