Fig. 7.
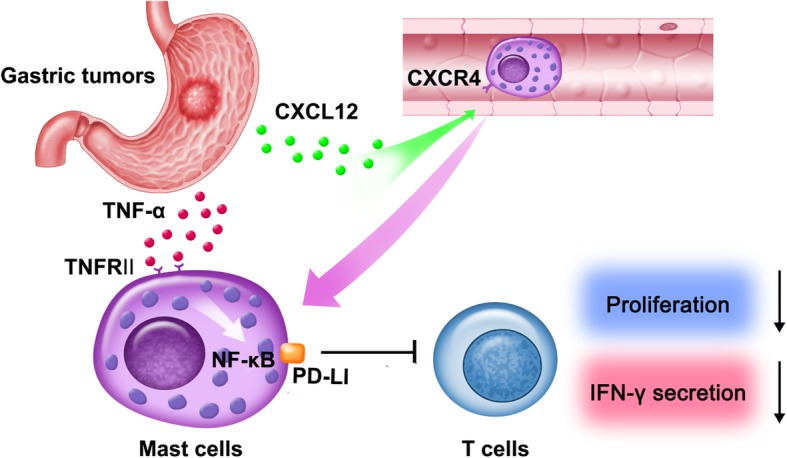
A proposed model of cross-talks among mast cells, T cells, and tumor cells leading to mast cell-mediated immunosuppressive and protumorigenic effects in the GC microenvironment. CXCL12-CXCR4 chemotaxis mediates the recruitment and accumulation of mast cells into the GC microenvironment, which could be up-regulated PD-L1 expression via NF-κB signaling pathway activation by tumor-derived TNF-α. Mast cells inhibit T-cell proliferation and function in a PD-L1-dependent manner in GC, which promotes GC progression
