Figure.
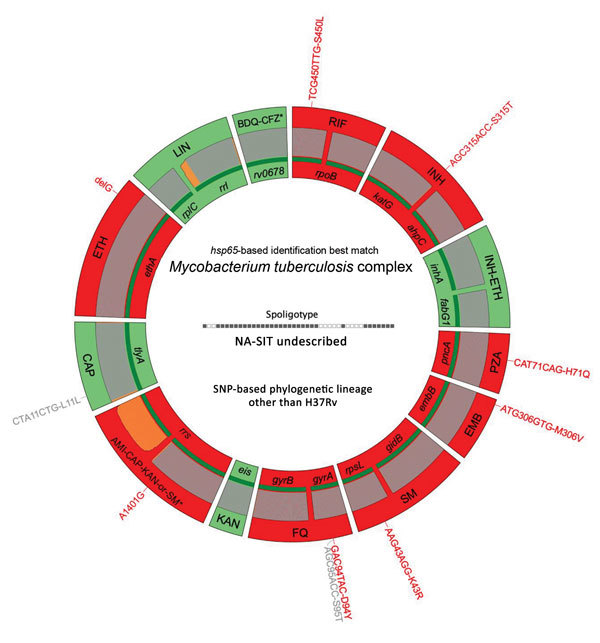
Deeplex-MycTB (GenoScreen, https://www.genoscreen.fr) results identifying an extensively drug-resistant genotypic profile in an isolate from a tuberculosis (TB) patient in Lebanon. Results correspond to TB patient no. 185 in Table 2. Target gene regions are grouped within sectors in a circular map according to the drug resistance with which they are associated. Red indicates target regions in which drug resistance-associated mutations are detected (red text around the map), whereas green indicates regions where no mutation or only mutations not associated with resistance (gray text around the map) are detected. Dark green lines above gene names represent the reference sequences with coverage breadth above 95%. Limits of detection (LOD) of potential heteroresistance (reflected by subpopulations of reads bearing a mutation), depending on the coverage depths over individual sequence positions, are indicated by gray (LOD 3%) and orange (variable LOD >3%–80%) above the reference sequences. Information on mycobacterial species identification, based on hsp65 sequence best match, and genotype of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strain, based on spoligotype and lineage-defining phylogenetic SNP, are shown in the center of the circle. AMI, amikacin; BDQ, bedaquiline; CAP, capreomycin; CFZ, clofazimine; EMB, ethambutol; ETH, ethionamide; FQ, fluoroquinolones; KAN, kanamycin; LIN, linezolid; INH, isoniazid; PZA, pyrazinamide; RIF, rifampin; SM, streptomycin; SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism.
