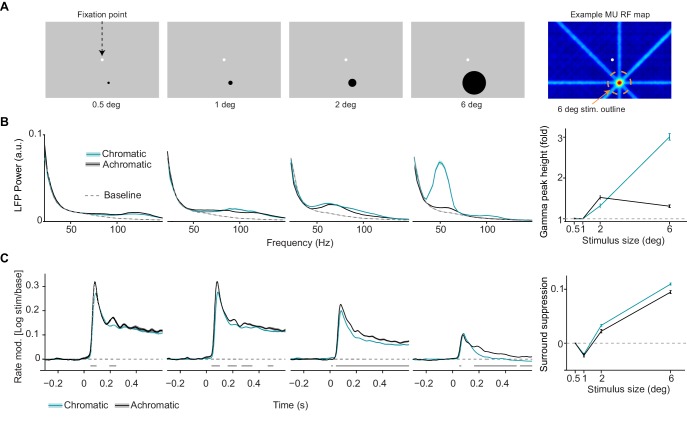
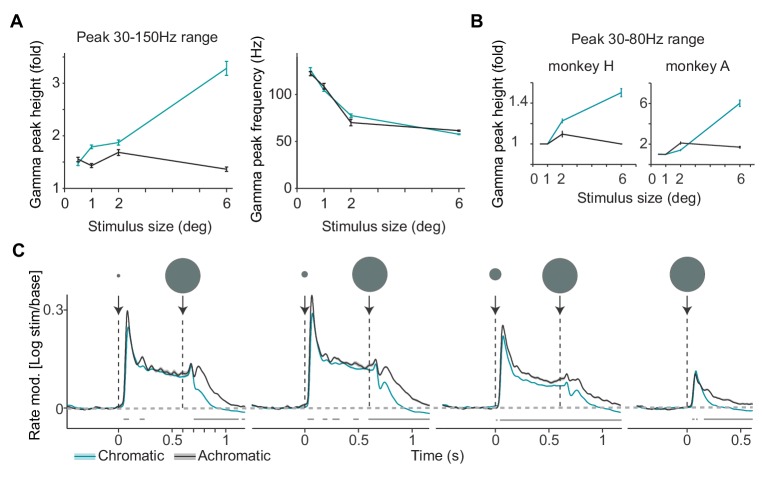
Figure 2. Dependence of LFP power spectra and MU firing activity on surface size.
(A) Illustration of experimental paradigm (Dataset 2, see Materials and methods; n = 9 sessions, 59.750.09/25.640.12 trials chromatic vs achromatic trials per condition in each session). Uniform surfaces of four different sizes were presented on a gray background screen. Fixation spot is enlarged for visibility. Right: Receptive field estimated with bar stimuli for a representative target channel, with the outline (orange dashed line) of the largest size stimulus (see Materials and methods). Note that the activation outside the RF is due to the use of large bar stimuli sweeping over the monitor. (B) LFP power spectra for different sizes and chromatic/achromatic conditions. LFP power spectrum estimated and normalized as in Figure 1C, but now using 300 ms epochs. Right panel shows the gamma-band amplitude as a function of size, estimated using a polynomial fitting procedure between 30 and 80 Hz (see Materials and methods). The difference between 6 and 0.5 deg stimuli was significantly larger for chromatic than achromatic condition (P0.05, bootstrap test, see Materials and methods). (C) Modulation of firing rate relative to baseline, expressed as , for different sizes and chromatic/achromatic conditions. Right panel shows surround suppression, which was defined as the difference in firing rate modulation between the 0.5 degree size and the other sizes.