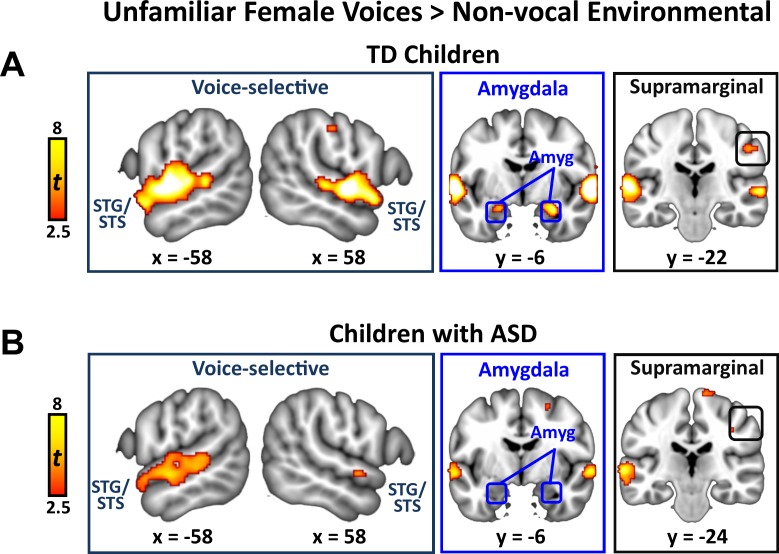
Appendix 1—figure 2. Brain activity in response to unfamiliar female voices compared to environmental sounds in TD children and children with ASD.
(A) In TD children, unfamiliar female voices elicit greater activity throughout a wide extent of voice-selective superior temporal gyrus (STG) and superior temporal sulcus (STS), bilateral amygdala, and right-hemisphere supramarginal gyrus. (B) Children with ASD show a reduced activity profile in STG/STS in response to unfamiliar female voices and do not show increased activity compared to environmental sounds in the amygdala.