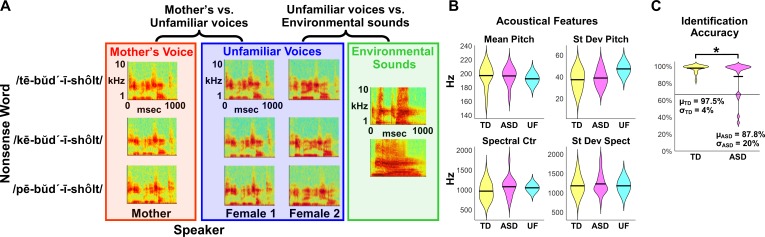
Figure 1. fMRI Experimental design, acoustical analysis, and behavioral results.
(A) Randomized, rapid event-related design: During fMRI data collection, three auditory nonsense words, produced by three different speakers, were presented to the child participants at a comfortable listening level. The three speakers consisted of each child’s mother and two control voices. Non-speech environmental sounds were also presented to enable baseline comparisons for the speech contrasts of interest. All auditory stimuli were 956 ms in duration and were equated for RMS amplitude. (B) Acoustical analyses show that vocal samples produced by the participants’ mothers were comparable between TD (yellow) and ASD groups (magenta) and were similar to the control samples (cyan) for individual acoustical measures (p>0.10 for all acoustical measures; see Appendix, Acoustical analysis of mother’s voice samples). (C) All TD children and the majority of children with ASD were able to identify their mother’s voice with high levels of accuracy, however five children with ASD performed below chance on this measure (see Appendix, Identification of Mother’s Voice). The horizontal line represents chance level for the mother’s voice identification task.