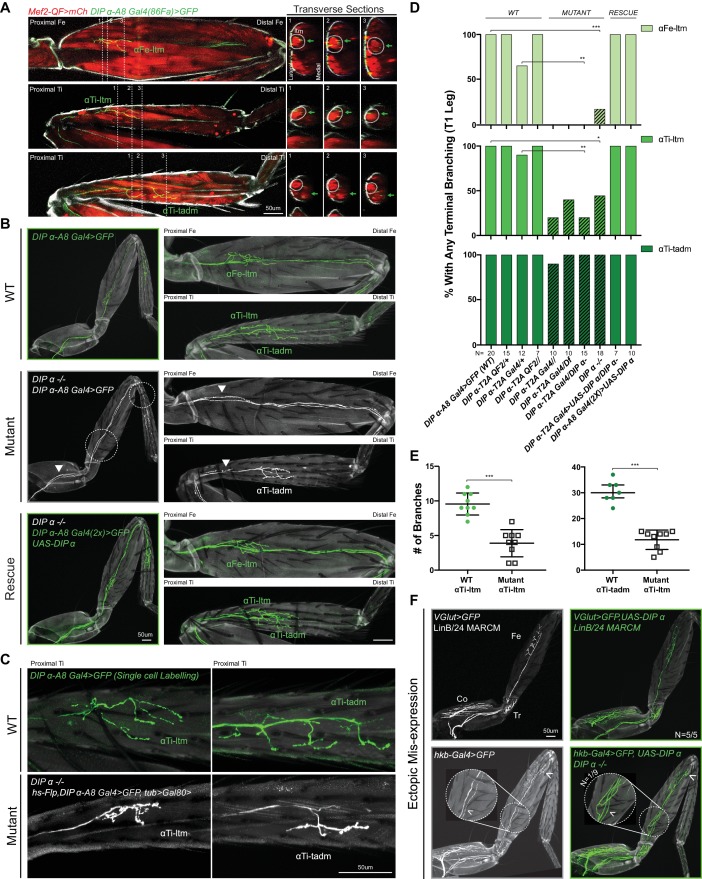
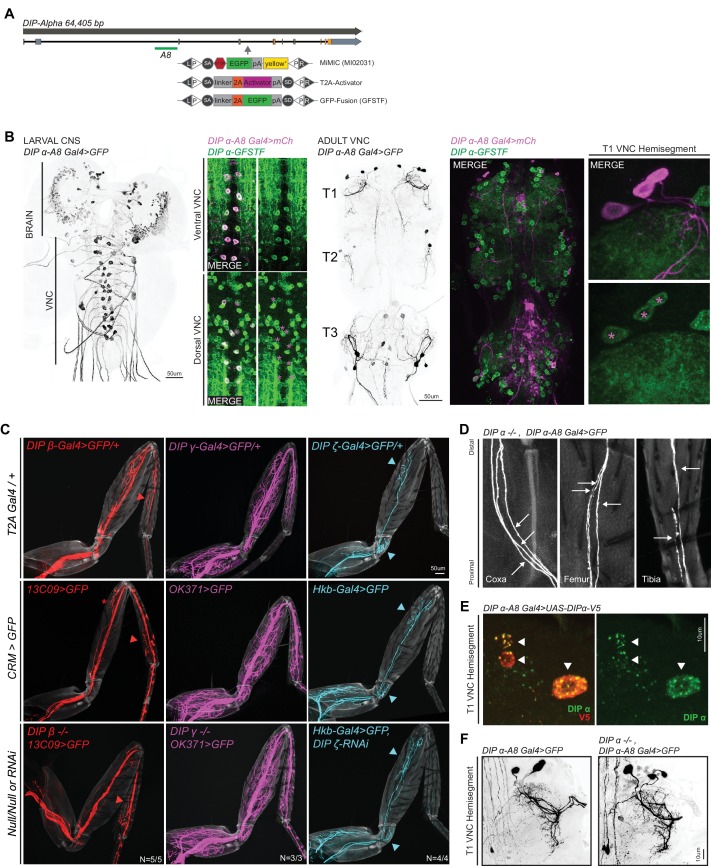
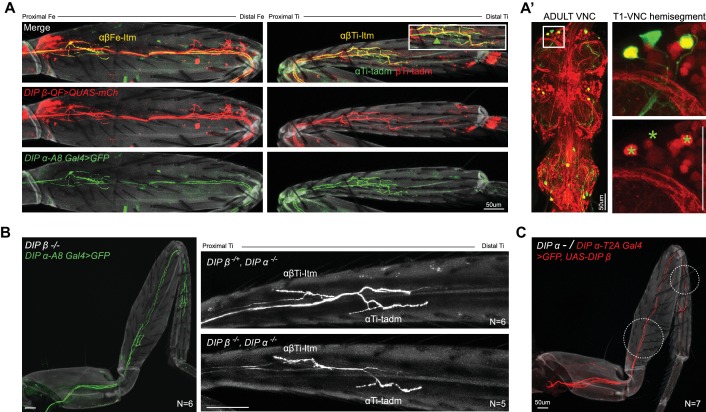
Figure 3. Effects of mutating DIP-α on the terminal branching of α-leg MNs.
(A) Left Column: Proximal-Distal (P–D) oriented Fe and Ti T1 adult leg segments depicting axon muscle-targeting of three DIP-α expressing leg MNs labeled by DIP-α-A8-Gal4(86Fa)>20XUAS-6XGFP (green) (Figure 3—figure supplement 1D) (See Materials and methods). Muscles are labeled using Mef2-QF > 10XQUAS-6XmCherry (red); Grey; cuticle. MNs are named according to the muscle target (αFe-ltm, αTi-ltm, and αTi-tadm) (Soler et al., 2004). Right Columns: Transverse sections of Fe and Ti leg segments at specific locations along the P-D axis, corresponding to the numbered white dotted lines on the left, depicting terminal branching (green arrows) on the Fe and Tiltms (encircled by white dotted lines) and tadm. (scale bar: 50 μm). (B) Terminal branching of the T1 α-leg MNs labeled by DIP-α-A8-Gal4(86Fa)>20XUAS-6XGFP in wild type (WT), DIP-α mutant and rescue contexts. Left; T1 legs; Right; Fe and Ti leg segments (axons; green (WT/rescue) or white (mutant), cuticle; grey). Absence of terminal branching of the α-ltm MNs in the DIP-α mutant T1 leg is indicated by white dotted circles; White arrowheads demarcate axons reaching the vicinity of their muscle targets (refer to Figure 3—figure supplement 1D). (scale bar: 50 μm). (C) Intermediate terminal branching defects in T1 legs displayed by αTi-ltm and αTi-tadm in DIP-α mutants. Single cell labeling of αTi-ltm and αTi-tadm terminal branches in the T1 proximal Ti is shown in WT (green) and DIP-α mutant (white). (scale bar: 50 μm). (D) Quantification of mutant phenotypes (αFe-ltm, light green; αTi-ltm, medium green; and αTi-tadm, dark green) in WT (N = 20), mutant (diagonal lines) and rescue contexts (N = 7 to 20) using a DIP-α null, chromosomal deficiency and MiMIC-T2A-Gal4/QF as indicated. Statistical significance was determined using Fisher’s exact test: *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001 (E) Quantification of number of branches on αTi-ltm and αTi-tadm single-cell samples in WT and DIP-α mutant contexts using genotypes indicated in Figure 1C. Statistical significance was determined using a two-tailed unpaired t-test for αTi-ltm samples, where error bars represent mean ± SD and a Mann-Whitney U test for αTi-tadm samples, where error bars represent median ± interquartile ranges. ***p<0.001 (F) Ectopic expression of DIP-α in LinB/24 leg MNs targeting the Coxa, Trochanter and Distal Fe using OK371-Gal4 MARCM (Top) or an enhancer trap hkb-Gal4 (Bottom) which also labels an additional leg MN targeting the distal Fe (white arrowhead). Normal axon targeting of LinB/24 leg MNs (white) is shown on the left without any terminal branching at the Fe-ltm. However, in a rare case (N = 1/9), ectopic expression of DIP-α using hkb-Gal4 in a DIP-α mutant background caused ectopic branching at the Fe-ltm (white arrowhead within magnified inset). (scale bar: 50 μm).